Essential Checklist for Custom Injection Molding Projects
Before embarking on a custom injection molding project, there are several key factors to consider. These include choosing the right materials, deciding on the surface texture, and establishing acceptance standards for the product’s appearance and dimensions.
To assist with these preparations, this article provides a detailed checklist for reference. If you need more information on any specific aspect, you can click on the links within the article for a deeper dive into those topics. Let’s get started on this journey.
Expertise meets affordability at Boyan for Custom Injection Molding. In need of our services? Reach out now!

What is custom injection molding
Custom injection molding is a process that involves designing and manufacturing plastic parts based on specific requirements.
This method uses molten plastic injected into a mold, which then cools and solidifies to form the part. It is widely used in manufacturing plastic components of various sizes and shapes, such as toys, automotive parts, and medical devices.
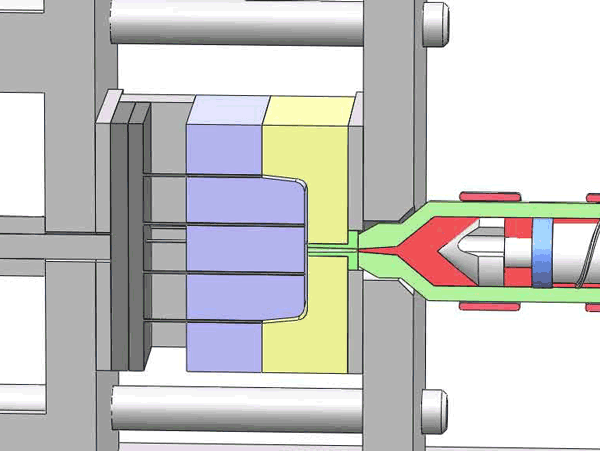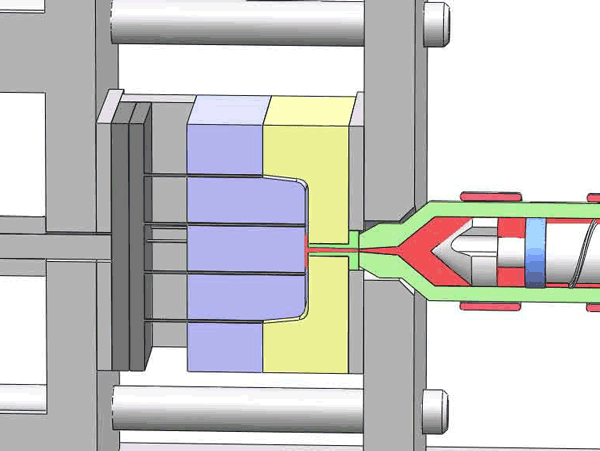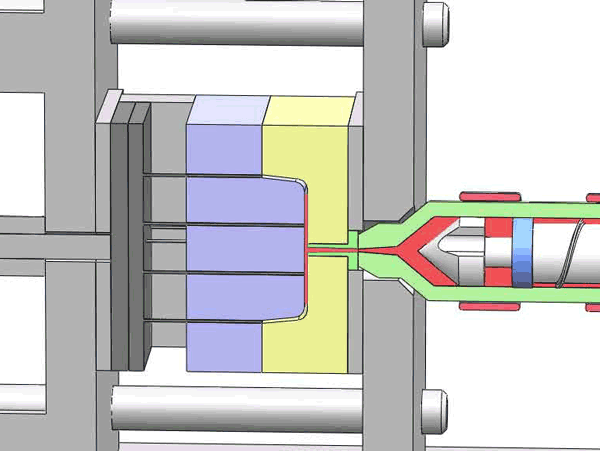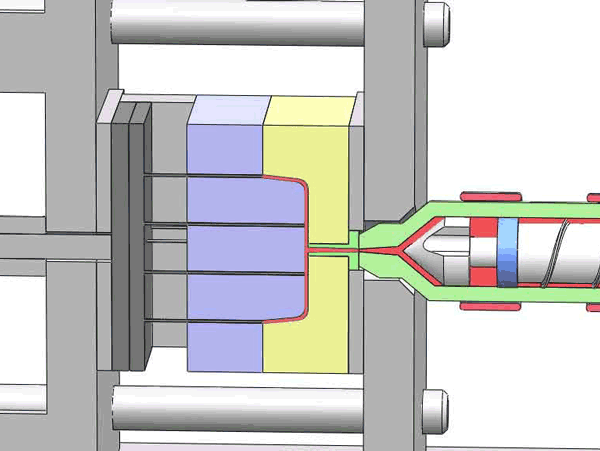
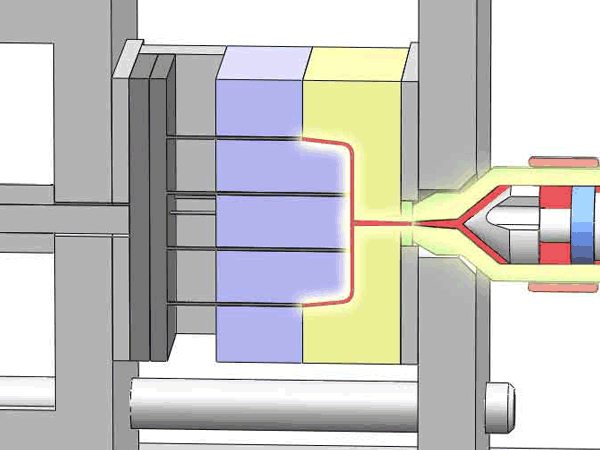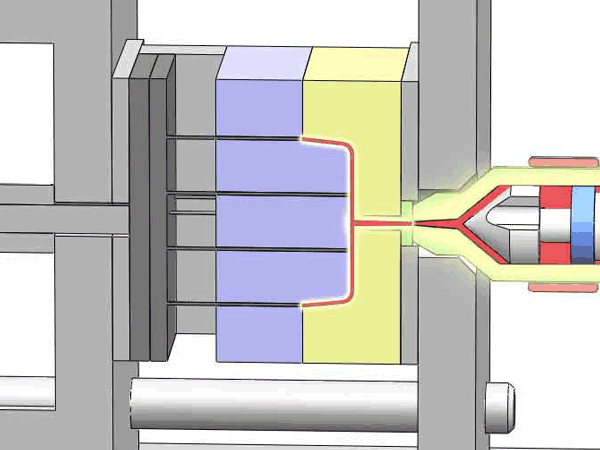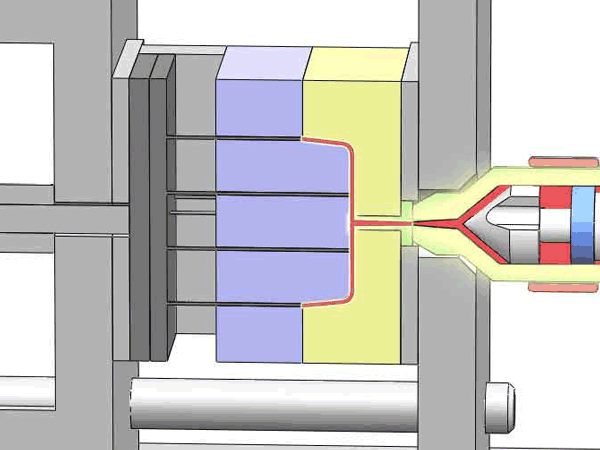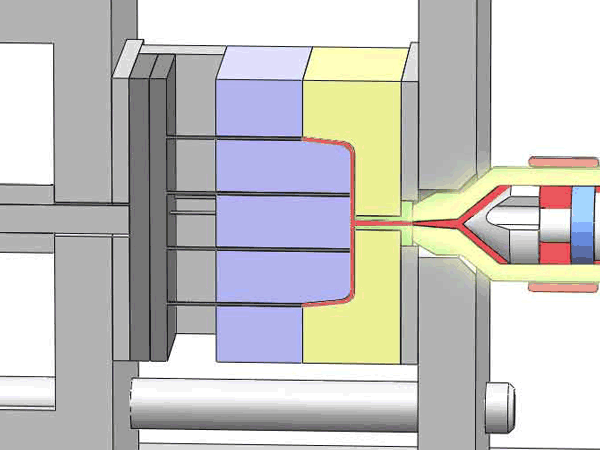
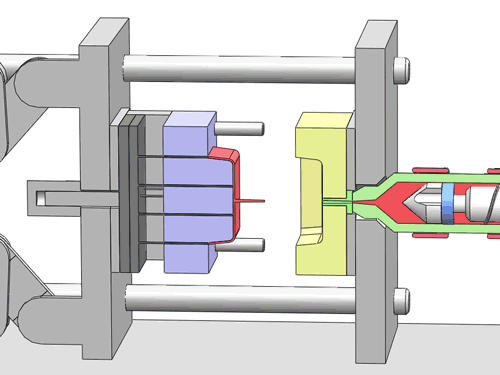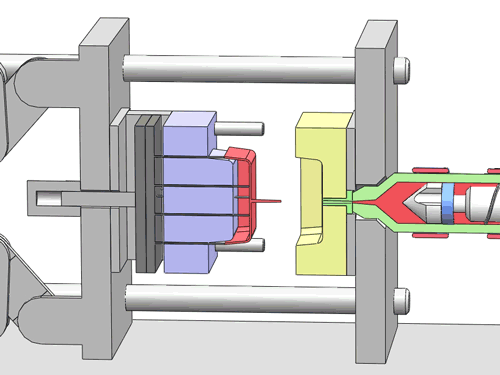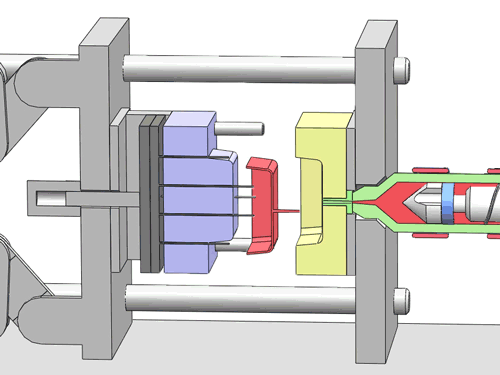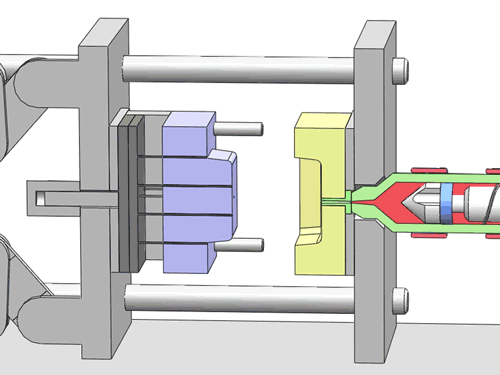
Categorization of your custom injection-molded components
In the field of injection molding, various types of products require different processing methods and suppliers due to their unique characteristics and application demands. These different types of injection molding products often face similar risks of molding defects and take corresponding measures to mitigate these risks.
Here are various categories of injection molding. Find the type that best suits your product.
Thick Wall Injection Molding
This type of injection molding is usually used to enhance the strength of the product. Special attention is needed in the processing to ensure uniform distribution of the material to avoid defects due to uneven wall thickness.
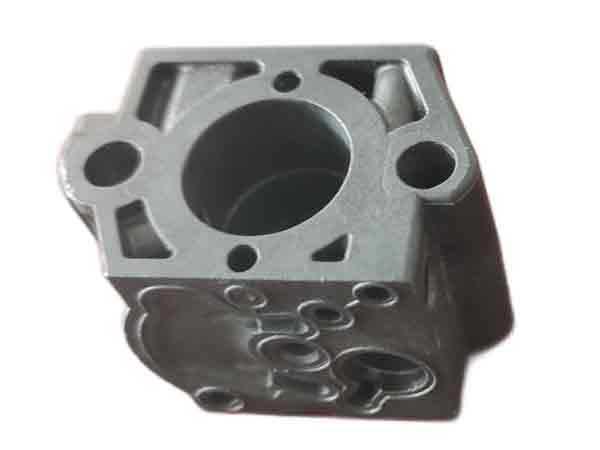


Transparent Product Injection Molding
For transparent products that need to maintain a good appearance, avoiding flow marks and gate blush is crucial. This requires precise control of material flow and cooling speed during the injection process.
Overmolding/Two-shot Injection Molding
Suitable for plastic products that require two different materials or colors. This method involves a second injection molding process following the first, to achieve a tight bond of the materials.
Insert Molding
This method involves embedding metal or other material inserts into the injection molded product. It’s often used in products that require metal threads, enhanced mechanical properties or electrical conductivity.
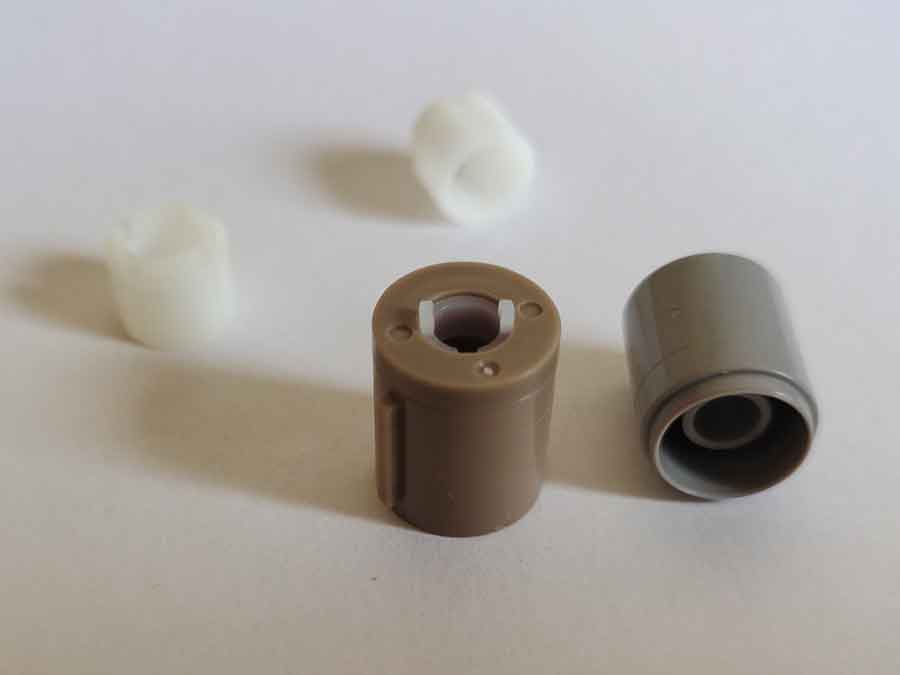
Micro Injection Molding
For extremely small parts, the precision of the injection mold is crucial. Specialized injection molding machines are often required to manufacture these types of products.
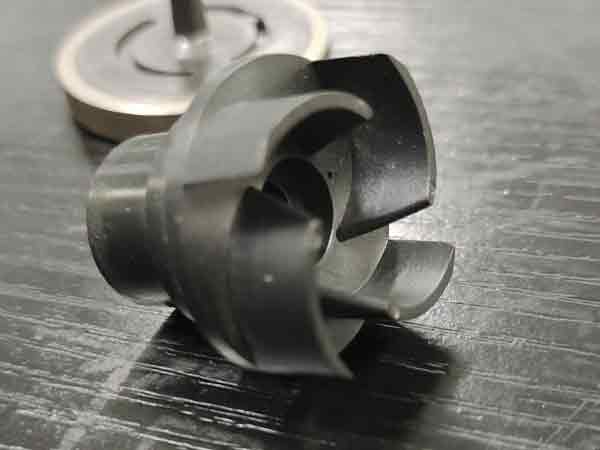


Precision Injection Molding
This type of injection molding is suitable for scenarios that demand high precision in product dimensions, such as electronic components, automotive parts, plastic gears, and more. Precision injection molding tests both the accuracy of the molds and the control over the injection molding process.
The above classifications are not completely independent, for instance, micro injection molding generally falls under precision injection molding, while overmolding might also include transparent product injection molding. However, these categories provide a general direction for product development, helping to find suitable processing methods and suppliers.
Most Common Plastics to be Used
In injection molding, plastics are broadly classified into three categories: thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, and elastomers.
Thermoplastics are most commonly used, further divided into general-purpose, engineering, and special engineering plastics.
- General-purpose plastics: like PE, PP, PVC, PS, and ABS, are ubiquitous in everyday products.
- Engineering plastics: such as PC, PA, PBT, PPO, and POM, offer enhanced mechanical and heat-resistant properties, ideal for mechanical and electrical parts.
- Special engineering plastics: including LCP, PSU, PI, PPS, and PEEK, are reserved for high-end applications due to their superior performance.
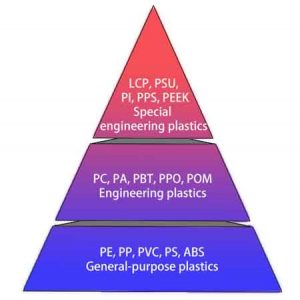
Each type of plastic is pivotal in determining the quality and suitability of injection molded products for specific applications.
Establishing Quality Requirements for Products
Before proceeding with custom injection molding, it is crucial to define the quality requirements of the product. Effective communication of these requirements with the mold manufacturer ensures that the product meets the anticipated standards.

Consideration of Aesthetic Requirements
The aesthetic needs vary depending on the usage scenario and product positioning. For instance, internal components might not require stringent aesthetic considerations, whereas externally visible parts should meet certain appearance standards.
This also includes considerations for color and surface finishes. Light-colored products are generally less sensitive to injection molding defects, while darker ones, especially black, tend to reveal flaws more easily. Regarding surface finishes, high-gloss surfaces are more prone to showing imperfections, whereas textured surfaces are more forgiving and can better conceal minor flaws.
Dimensional Accuracy
Depending on the function of the product, key dimensions and their permissible tolerances should be established.
Setting tolerances requires caution – too high or too low tolerances should be avoided. Excessively high tolerances may be difficult to achieve, while too low tolerances might reduce the quality of use.
In determining tolerances, besides relying on the technical experience of designers, actual usage testing is key, as it provides a more accurate range of tolerances.
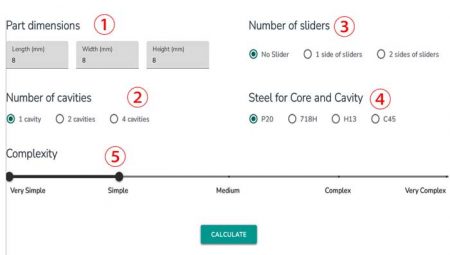
Selecting the appropriate mold material is critical for the cost and quality of injection molds. The choice of mold steel depends on different production needs and product characteristics.

Different Grades of Mold Steel
- For injection molds used in small batch production, cost-effective mold steels like P20, 718, or even C45 can be chosen. This approach satisfies production needs while controlling costs.
- Products requiring high surface quality and dimensional accuracy need higher-priced but superior quality mold steels, such as 718H, 2083H, S136H, etc. These steels offer better surface finishing and dimensional stability.
- For processing high-temperature materials or plastics with glass fibers, molds require steel with higher hardness, like H13, SKD61, 2316, etc. Despite their higher cost, these steels can endure greater pressure and temperatures, ensuring mold durability and stability.
Pre-Hardened and Through-Hardened Tools
Molds are primarily divided into pre-hardened and through-hardened types. Pre-hardened molds have fewer processing steps, a shorter production cycle, and no need for heat treatment, which lowers the cost. In contrast, through-hardened molds have higher overall hardness and are suited for more demanding production environments, but they come with relatively higher manufacturing costs.
In conclusion, when selecting mold materials, it’s important to weigh the cost against quality, based on the specific needs and budget of the product. Choosing the most suitable mold steel is crucial to ensure both the quality and economic efficiency of injection-molded products.
Selecting the appropriate surface finishes for a product is an important consideration before starting a custom injection molding project. The surface texture of plastic parts not only affects the product’s appearance but also its tactile feel and practicality.
Common Surface Finishes
The most common surface finishes include polished and textured surfaces. Polished surfaces are smooth and shiny, suitable for products requiring a sleek appearance. Textured surfaces have a certain degree of roughness, providing a good tactile feel and visual effect. In addition, more diverse textures like leather, wood grain, or various geometric patterns can be chosen. These textures can give the product a more unique look and characteristics.

Surface Finish Standards Guidelines
Common standards for defining surface textures include SPI, VDI3400, and MT. Many mold texture manufacturers also offer a variety of custom templates to choose from. Therefore, it’s crucial to communicate thoroughly with the manufacturer when determining the surface texture.
Based on the specific needs and desired effects of the product, the most suitable surface texture design should be selected. Although this step may take some time, it’s vital for the final quality and market performance of the product.

Before initiating mold production, it is crucial to conduct a comprehensive review of the injection molding product and its mold design. This process is known as “Design for Manufacturing” (DFM).
Since mold production strictly follows the design blueprints, ensuring the rationality and accuracy of the design is an essential step.
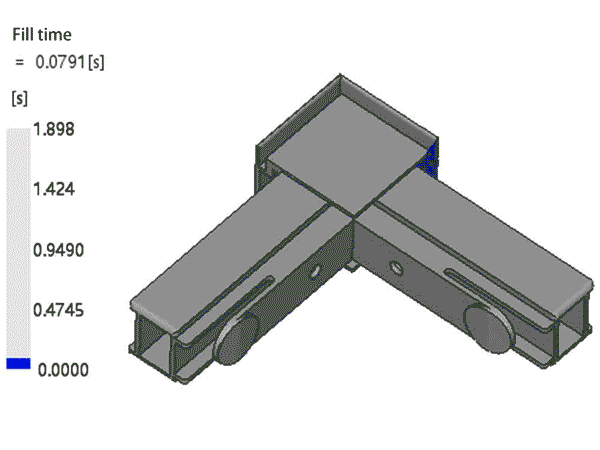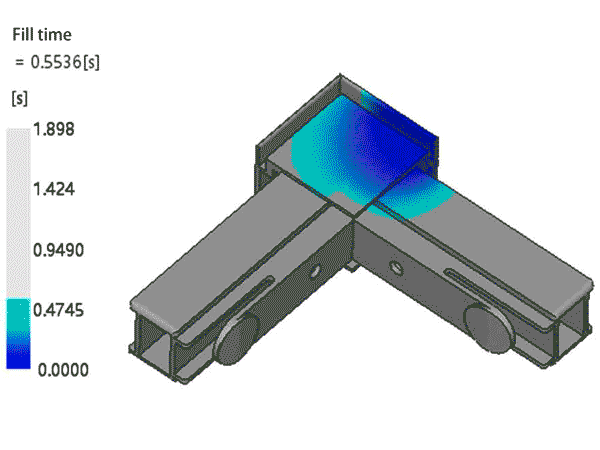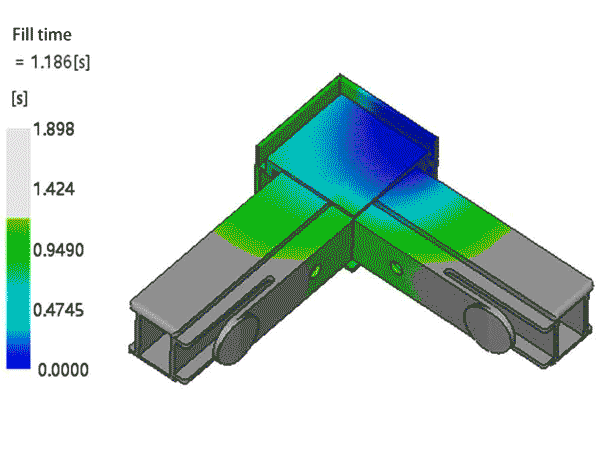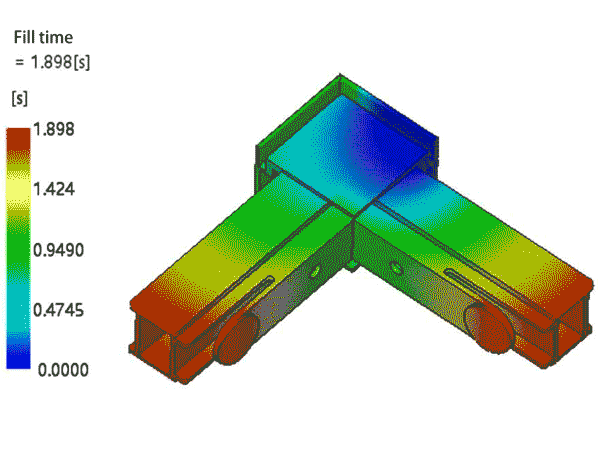
Product Design Review
The inspection of product design includes, but is not limited to, uniformity of wall thickness, rib design (considering the thickness and height of ribs), and draft angles. These elements directly impact the overall quality of the product and the ease of production.
Mold Design Review
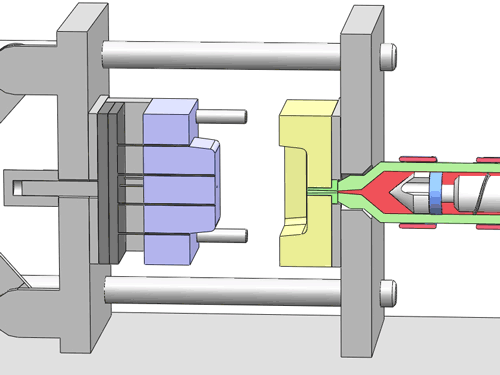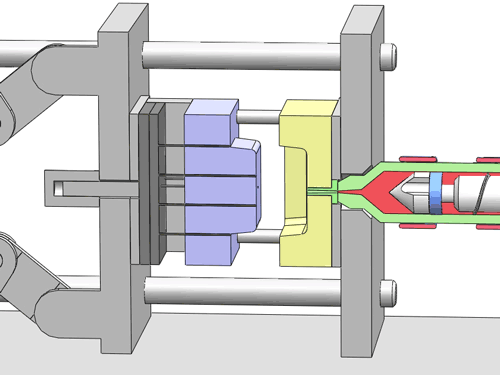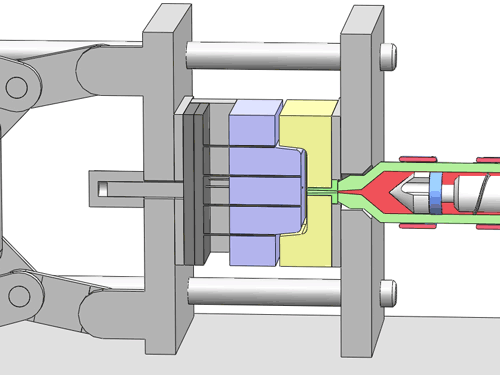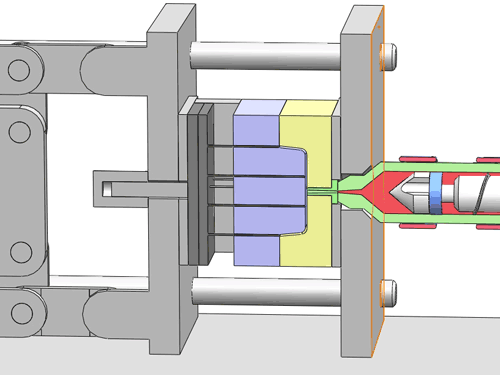
For mold design, aspects that need detailed examination include the type and location of the gate, the type and position of ejector pins (components used to eject the finished product), the location of parting lines, and the design of sliders. These details are directly related to the efficiency of mold production and the quality of the final product.
Although these inspections cannot completely guarantee the absence of flaws in the design and some adjustments and repairs might still be needed during the later stages of mold making, thorough pre-checks can significantly reduce the occurrence of design defects, thereby enhancing product quality and reducing production costs.
Mold Costs and Production Processing Costs
Cost analysis is a critical aspect of custom injection molding projects. Costs are mainly divided into two major parts: the cost of the injection mold and the cost of product processing.
Mold Costs for Small Batch Production
For injection-molded products in small batch production, mold costs usually constitute the major expense. Given the significant initial investment in molds and the long production cycle, effectively reducing mold costs becomes a priority.
Mold costs include material costs, processing costs, design fees, and so forth. To lower these costs, one strategy is to choose more economical mold steels, and another is to use family molds.
Explore the efficiency of our online injection mold cost calculator and receive instant cost estimations!
Production Processing Costs for Large Volume Production
In the case of injection-molded products for large volume production, the cost of product processing becomes predominant. The focus shifts to improving mold quality and extending its lifespan to ensure continuous production. Sometimes, even spare molds are needed to prevent production disruptions in case of mold issues. Methods to reduce production costs include shortening the injection molding cycle, increasing the number of parts produced per mold, using composite molds, implementing automation equipment like robotic arms to reduce labor costs, and maintaining efficient mold operation.
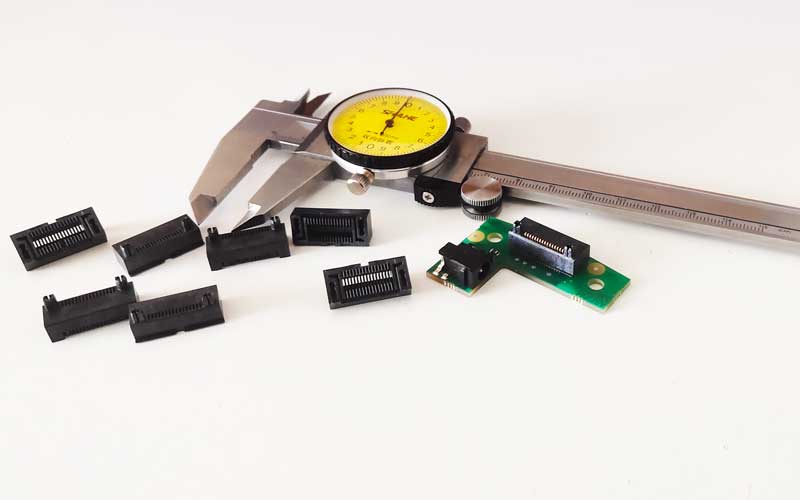
There are several key steps to follow in the quality inspection process of injection molded products. These steps include both appearance and dimensional inspections, and they require professional knowledge as well as a high level of responsibility.
Appearance Inspection
This usually relies on visual inspection, where products are examined by eye to identify any defects. In large-scale production, photographic systems can be used for automated inspections to improve efficiency. However, manual visual inspection remains indispensable, as some subtle defects may only be detectable by a trained eye.
Dimensional Inspection
Given the flexibility and elasticity of plastic products, special gauges (like go/no-go gauges) are often used to check product dimensions, or assembly with mating parts is used for testing. Additionally, for more precise measurements, tools like calipers may be employed.

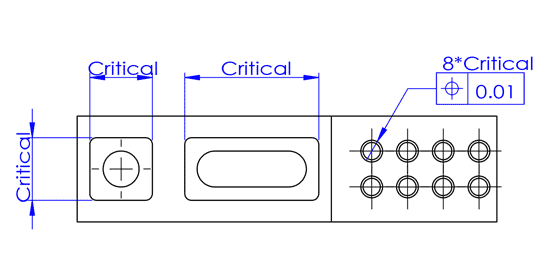
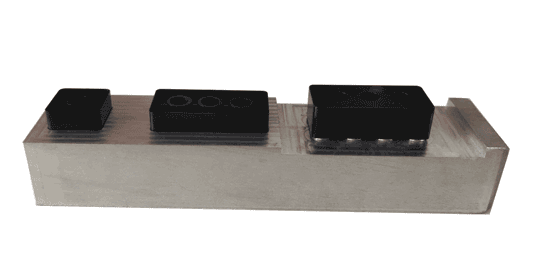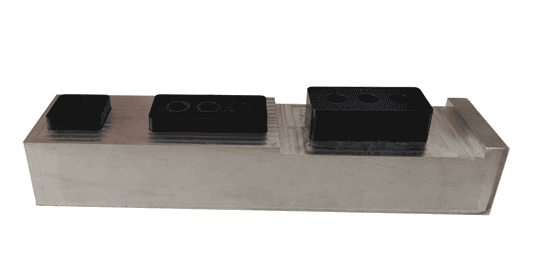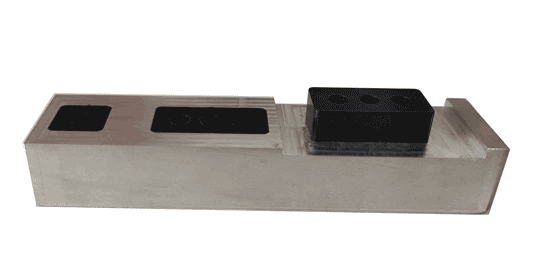
In summary, inspecting the quality of injection molded products requires not only sufficient professional knowledge and experience but also a meticulous attitude and a strong sense of responsibility. Through these detailed inspection steps, the product can be ensured to meet the established quality standards.
Post-Processing in Injection Molding
After the injection molding process, plastic products often require a series of post-processing operations to meet specific functional and aesthetic requirements.
Surface Treatment
This includes surface coating and printing. Surface coating techniques, such as painting and electroplating, are used to enhance the appearance and durability of products. Surface printing involves processes like silk screen printing, pad printing, and laser marking, which add patterns, text, or logos to the product.

Welding Processes
Methods like ultrasonic welding, friction welding, and heat welding are used to join different plastic parts into a single unit, improving the product’s structural strength and integrity.
Mechanical Processing
This step includes milling to remove gate scars or laser cutting, and drilling holes in parts with complex structures where creating them directly with sliders is challenging.
Removing the sprue by Laser Cutting and CNC Milling


Note: The advantage of using laser cutting to remove the sprues from injection molded parts is its speed. It can work in tandem with robotic arms, offering high efficiency. However, there may be slight vertical striations at the cut. CNC milling, on the other hand, can achieve very smooth edges, leaving hardly any visible marks.
In conclusion, these post-processing operations play a crucial role in enhancing the overall quality and appearance of injection molded products and are an indispensable part of the injection molding process.
Product Packaging
If only shipping product parts, plastic bags can be used for packaging to prevent scratches. For small parts that are unlikely to scratch each other, multiple parts can be placed in the same plastic bag.
Individual Product Packaging
For single, complete products, packaging options typically include cardboard boxes, color boxes, double blister packs (a type of plastic packaging), and blister card packaging. These methods not only protect the product from damage but also display product information and attract customer attention.
Packaging for Parts
If only shipping product parts, plastic bags can be used for packaging to prevent scratches. For small parts that are unlikely to scratch each other, multiple parts can be placed in the same plastic bag.
Bulk Packaging
For bulk packaging, the design generally involves cardboard boxes. The design should consider how to neatly place products while maximizing space utilization. For products of different sizes, it’s best to use boxes of the same size or ones that can be stacked together, which facilitates transportation and storage. Differently sized boxes might lead to inefficient stacking, affecting shipping efficiency. Therefore, it’s important to design appropriate box sizes and stacking schemes using software before shipping the products.
Cardboard Box Design Tips
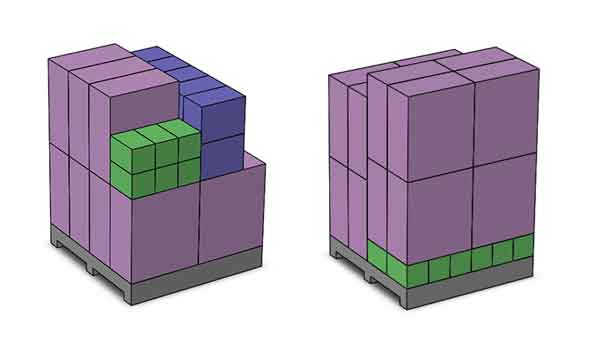
If there are cardboard boxes of different sizes, they should be stackable and able to be placed on pallets to avoid issues with stacking. The key is to maintain a proportional relationship in the length, width, and height of the boxes. The attached image demonstrates how three different sizes of boxes can be stacked together.

The dimensions of the cardboard boxes must be adapted to fit the standard sizes of pallets, which are typically 0.8 meters, 1 meter, or 1.2 meters. Therefore, sometimes it’s necessary to adjust the arrangement of products inside the boxes to match the pallet sizes, which may result in not fully utilizing the internal space of the boxes.
Finally, product packaging should consider not only product protection but also the convenience and cost-effectiveness of transportation. Proper packaging design ensures safe delivery of products and can also enhance brand image.
Summary
With all being introduced above, this article has traversed from design intricacies to the final packaging, offering insights into each step of the process. As a foundational technique in producing diverse plastic components, its role in shaping the future of manufacturing remains pivotal and ever-evolving.