What is Micro Injection Molding?
Micro injection molding refers to the production of highly precise plastic components where the molded products typically weigh less than 0.01 grams to several grams. Actually, they may not be exceptionally small in overall size, but they exhibit extremely fine details and demanding dimensional accuracy. Such plastic items can be categorized as micro injection molding products.
When compared to standard injection molding, micro injection molding imposes greater demands on both the molds and the molding machines.

Applications of Micro Injection Molding
Micro injection molding finds diverse applications across various industries, including:
- Micro Gears: Producing small, precise gears used in various devices and systems.
- Electronic Connectors: Crafting miniature connectors for electronic equipment.
- Micro Switches: Manufacturing tiny switches used in electronics.
- Housings: Creating compact housings for electronic and mechanical components.
- Automobile Rotation Dampers: Producing components for automotive systems.
- Pen Parts: Crafting small parts for pens.
- Drone Parts: Manufacturing precise components for drones.
- Headphones: Creating intricate components for headphone assembly.
- Medical Equipment: Developing critical parts for medical devices, including catheter tips, syringe components, microfluidic devices, and surgical instrument components.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of micro injection molding in producing small, high-precision plastic components used in a wide range of industries and products.



Unique Methods for Micro Injection Molding Molds

Utilizing mold inserts rather than machining in a single piece
For molds used in micro injection molding, due to many features being only a fraction of a millimeter in size, it’s necessary to adopt methods different from the conventional ones for mold making. Apart from using high-precision machining equipment, it’s common to use mold inserts, meaning different features are processed separately and then assembled together. This approach simplifies the machining process and reduces costs.
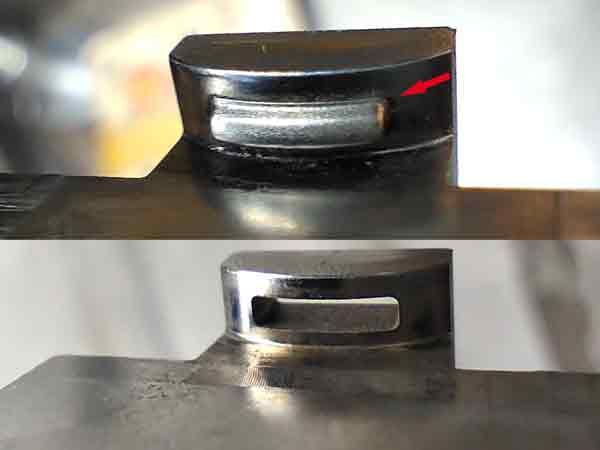
An example of forming an undercut feature through the use of inserts
For example, consider an undercut structure in the product shown below. If processed as a single piece, it would result in overly large transition radii. These would occur at the inner corners. This could prevent the product from securely snapping and locking with its mating parts.


This is because single-piece machining, whether using milling cutters or electrodes, would inevitably create rounded edges at sharp corners, resulting in unwanted round arcs at the inner corners of the mold. Using inserts allows for achieving perfect sharp angles at these inner corner transitions.


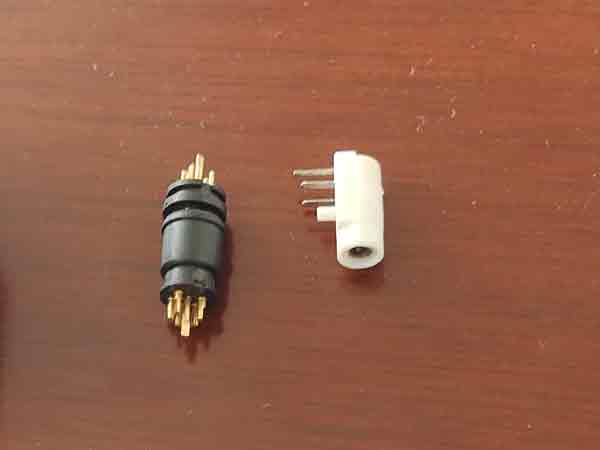
More examples of micro-molded electronic connectors
Electronic connectors are one of the most common applications in micro injection molding. Initially, the metal contacts within the connector are stamped and plated in rolls. Then, insert molding is performed around the metal contacts while they are still in roll form. Finally, these metal pins are formed and separated on a stamping machine.
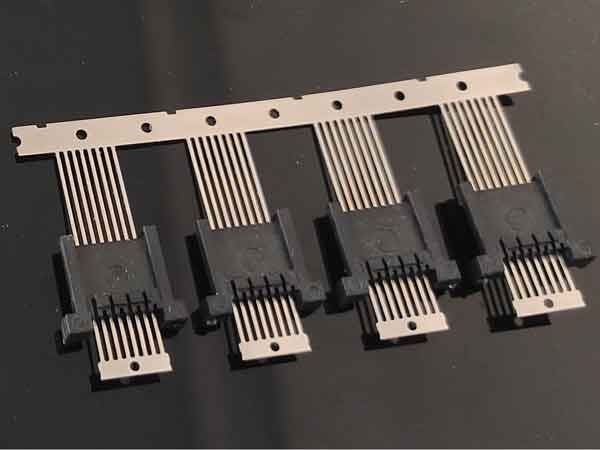
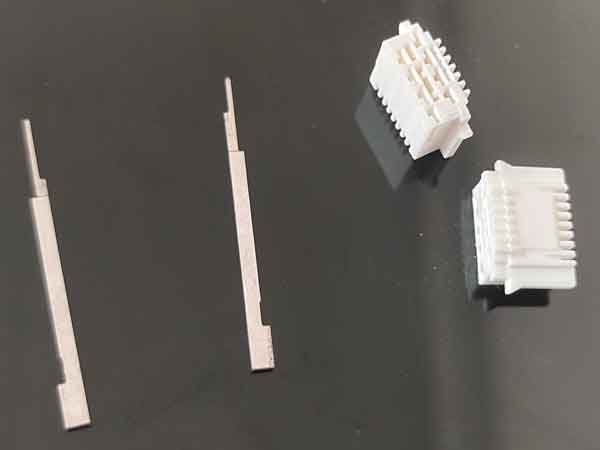
Some features on these connectors are very small, for example, the slot widths are only between 0.2 to 0.3mm. These specific traits on the mold inserts are machined using precision grinders with grinding wheel widths of only 0.2-0.3mm.
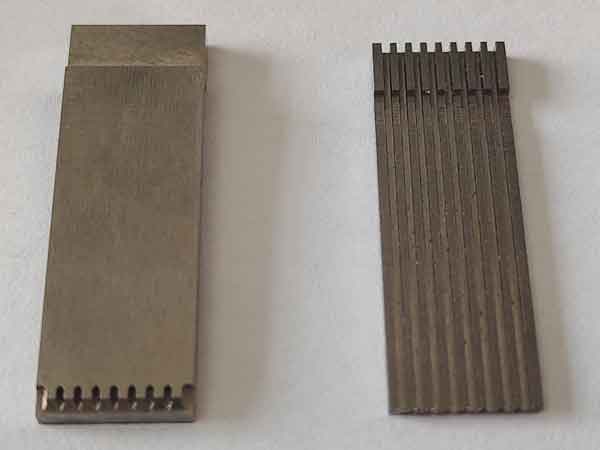


Similarly, the recessed holes on the mold inserts, which are roughly the same size, are processed using mirror electrical discharge machining (EDM).

It’s easy to see that if these features were not processed using separate inserts but as part of the entire mold, the complexity of the task would significantly increase.
Dimensional Inspection of Molds:
When inspecting the dimensions of these molds, a projector is preferred over a CMM (three-dimensional coordinate detector). The reason for this choice is that the probe fillet of the latter is typically too large to accurately measure the fine features of these molds.
Conclusion: The production of precision injection molds for tiny parts necessitates not only high-precision processing equipment but also highly skilled engineers. Both elements are critical and cannot be substituted. This combination of advanced technology and expert craftsmanship is essential to meet the exacting standards of micro injection molding.
How to Inspect Tiny Injection Molded Parts
When it comes to the production of tiny injection molded parts, there are three critical requirements to ensure quality and precision:
Precise Detailing: Precision is key. Every aspect of the original design must be accurately replicated. For instance, if the design specifies clear corners with an arc radius of 0.05mm, it’s crucial that this measurement is met. Deviations, such as an increase to 0.1-0.2mm, can lead to a loss of detail and a blurred appearance in the final product.
Dimensional Accuracy: The standard dimensional accuracy for ordinary injection molded parts is typically within the range of 0.1-0.2mm. However, for small precision parts, this accuracy needs to be less than 0.05mm. Maintaining this level of precision is vital for the functionality and fit of the component.
Weight Accuracy: The accuracy of weight in ordinary injection molding can achieve ±1% of the product’s weight. In precision injection molding, this accuracy tightens to ±0.5%, and for ultra-precision molding, it goes below ±0.3%. This parameter is crucial as it not only reflects the accuracy of the molding process but also indirectly indicates the overall precision of the part.
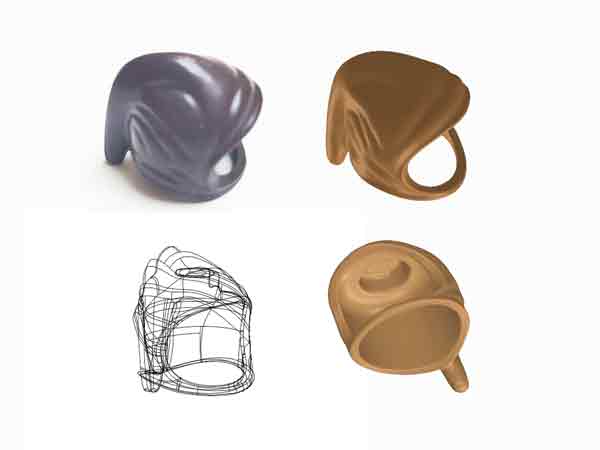
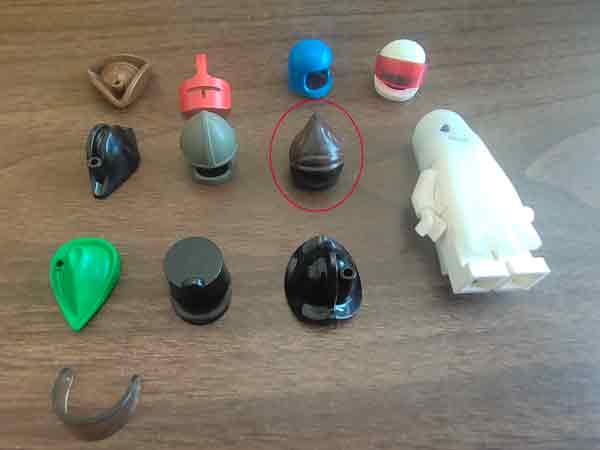
In some cases, tiny injection molded parts may primarily require precise detailing without as stringent demands for dimensional and weight accuracy. A classic example is the helmets of Lego toys, where the focus is on replicating exact appearance details.
Measuring dimensional accuracy in plastic parts can be challenging due to the material’s elasticity. Typically, pass-and-stop gauges are used for this purpose. On the other hand, weight accuracy is relatively easier and quicker to measure. It’s a useful indicator of the molding process’s precision and is often used as a key testing parameter.
Requirements for Injection Molding Machines
It’s important to recognize that standard injection molding machines may not always be suitable for micro molded parts, due to two specific requirements of micro injection molding.
- Smaller Screw Size: Micro molded products weigh only tenths of a gram or even less. Using a larger screw means the molten plastic stays too long in the high-temperature environment of the barrel, possibly causing molecular chain breakage. This can negatively affect the material’s properties.
- Higher Injection Pressure: To ensure the product fills the mold cavity and replicates every feature, micro injection molding requires comparatively higher injection pressure.

Machine Options Based on Production Needs
Depending on the order volume and weight of the micro-molded products being processed, two options are available:
- Option 1 – Using Standard Injection Molding Machines: For very small batches, the cost of changing screws or using a specialized machine may be higher. In such cases, it might be necessary to periodically remove some molten plastic to ensure it doesn’t stay in the barrel too long. However, for larger batches, it’s feasible to switch to screws with smaller diameters.
- Option 2 – Using Specialized Micro Injection Molding Machines: Well-known brands in this field include Sodick, Fanuc, and Toyo. These machines usually have a clamping force of only 40 tons, or even as low as 15 tons, compared to a standard 80-ton machine. They offer higher injection pressures, often exceeding 200Mpa and sometimes reaching up to 400Mpa.
Features of High-End Injection Molding Machines
These high-end machines come with several advanced features:
- All Electric mode: Most high-precision injection molding machines use all-electric mode, eliminating the need for a hydraulic system and using a private server system to control movement. This improves accuracy and reduces energy consumption.
- Screw-Plunger Hybrid Structure: This is adopted by some machines to ensure consistent plasticization, crucial for maintaining the quality of the final product.
- PID (Proportional Integral Differential) Temperature Control: This mechanism is vital for maintaining optimal temperatures throughout the injection molding process.
- Screw and Nut Mechanism for Mold Operations: These machines use a screw and nut mechanism for mold opening, closing, and ejection pin ejection. The precision of this mechanism is remarkable, with a transmission accuracy of up to 0.01mm.
- New Type of Force Sensor: This technology is employed to accurately control the injection back pressure, ensuring stable dimensional accuracy of the molded parts.
In summary, for small batches and when precision requirements are not stringent, general-purpose injection molding machines can be used, possibly with a smaller screw. Otherwise, it is necessary to opt for specialized micro molding precision injection molding machines.
Precautions to Consider in the Micro Injection Molding Process
The injection molding process for micro plastic products has distinct requirements compared to ordinary plastic products, especially in terms of temperature, pressure, and injection speed.
Temperature: Micro plastic products typically require a higher injection temperature to ensure the material’s fluidity and complete filling of the mold. Precise temperature control is crucial. This includes accurately adjusting the barrel temperature, mold temperature, and hot runner temperature. Such control is necessary to prevent issues like thermal degradation, thermal stress, and thermal deformation.
Pressure: Both injection pressure and holding pressure for micro plastic products are generally higher than those for standard plastic products. This is to overcome the increased resistance and high shrinkage rate in micro mold cavities. High-pressure control is essential, including precise management of the injection pressure’s size, segmentation, and switching points. Proper control helps avoid defects like short shots, flashes, shrinkage cavities, and warpage.
Injection Speed: Micro plastic products are usually injected faster than their regular counterparts to achieve rapid filling and even cooling. Controlling the injection speed is vital, including precise management of its size, segmentation, and switching points. This helps prevent issues like jets, burn marks, flow marks, and welding lines.
In summary, the injection molding parameters for micro plastic products demand high precision, efficiency, and stability. Achieving this requires the use of dedicated precision injection molding machines and specialized micro molds. These tools and techniques are essential for the successful production of high-quality micro plastic components.
Reverse Engineering of Tiny Injection Molded Products
Reverse engineering small plastic items is a fascinating yet challenging adventure. It’s like being a detective, piecing together three-dimensional drawings from actual products. But the smaller the item, the trickier the puzzle becomes.
The Hurdle of Scanning Technology: Imagine using a scanner to capture a product’s every detail in 3D. Works well for bigger items, right? But with tiny things, it’s a different story. Scanners struggle because they can’t pack enough detail into the tiny spaces between points. It’s like trying to read a book where half the letters are missing – you won’t get the full picture.
The Role of Designer Know-How and Handy Tools: This is where our designers shine. They dive in with their know-how, turning to manual 3D modeling and using tools like projectors and vernier calipers to nail down the exact sizes of important features. It’s a bit old school, but it works.
A Real-World Adventure – LEGO Toy Helmets: Let’s take LEGO toy helmets as an example. Our team, drawing on their experience and pooling their ideas for tweaks and improvements, set out to recreate these tiny marvels. Getting a carbon copy is tough, but the end result? A design that’s a spitting image of the original. This journey showcases the magic mix of tech, manual craftsmanship, and teamwork needed to reverse engineer these mini masterpieces.

Summary
In conclusion, micro injection molding demands precision in machinery, mold design, and process control, blending advanced technology with expert craftsmanship to create intricate, high-quality plastic components.