The importance of knowing the injection mold cost
If you’re considering outsourcing a plastic injection molding project, you might be curious about how to secure a reasonable price for the injection mold. In this article, we’ll break down the cost calculation for an injection mold. We’ll delve into the hourly rates associated with each manufacturing process, along with the key factors that influence the mold’s cost.
Our online mold cost calculator will help you determine an appropriate price for your mold and explore ways to potentially reduce the mold investment.
Empirical quotation method
A mold consists of many parts, each requiring various machining processes, making its cost calculation complex. While determining the cost of materials can be relatively straightforward and precise, calculating processing costs is more challenging.
Processing costs depend on the type of equipment used and the time it takes to complete the process. Accurately predicting processing time is difficult, whether through human estimation or using 3D simulation software. As a result, mold pricing often relies on estimates.
To provide a quotation for a mold, it’s necessary to first design the mold structure. Following that, you calculate the cost of materials, estimate machining and additional costs, and then finalize a quote for the mold.
Certainly, this estimate is neither arbitrary nor imprecise, due to the following reasons:
- The calculation of material cost is quite precise;
- The estimation of machining costs is derived from the mold’s dimensions and past experience with comparable products;
- The mold maker is aware that overestimating could result in losing this opportunity.
However, there remains a degree of uncertainty, which we will explore in more detail subsequently.
The foundational elements of injection molds
An injection mold consists of several precision-engineered steel parts. These parts are meticulously shaped and honed to specific dimensions and tolerances, then assembled to form a complete mold. This assembly serves as the vessel for injecting, shaping, cooling, and solidifying of molten plastic to form the finished part.
Although the complexity of injection molds may differ, with some displaying elaborate designs and multiple moving parts, their fundamental structure remains unchanged.
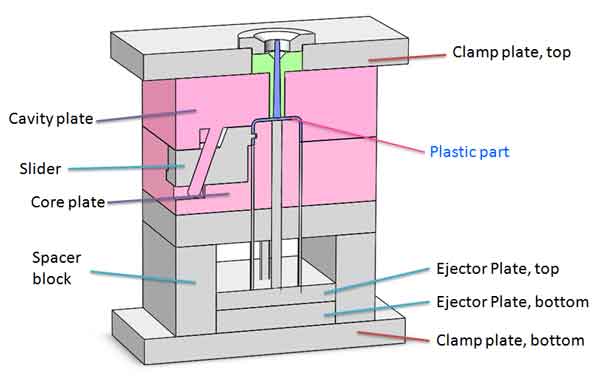
Essentially, an injection mold comprises the following parts, categorized into two main groups:
- Main components: Cavity plate, Core plate, Slider, Spacer block, Clamp plate (top and bottom), Ejector plate (top and bottom).
- Accessories: These include sliding pillar, ejector pins, sprue bushing, locating ring, springs, some molds will have hot runners, and so forth.
Here are some clarifications:
Upon closing, the Core Plate, Cavity Plate, and Slider form a sealed compartment where the plastic material is molded and solidified. Once the mold opens, these parts disengage, allowing the release of the solidified plastic item.
Due to the common occurrence of undercuts in the designs of plastic parts, injection molds frequently include sliding mechanisms. These mechanisms are primarily of two types: one that transforms vertical movements into horizontal ones using inclined rails, and another that employs hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders for movement.
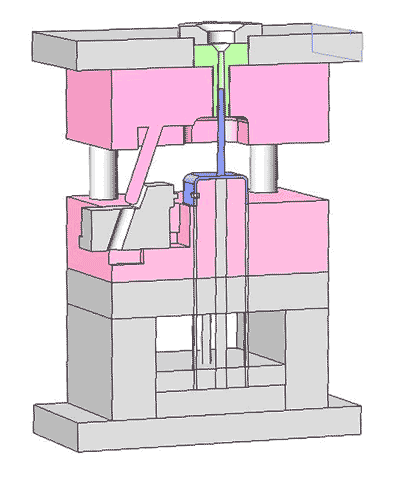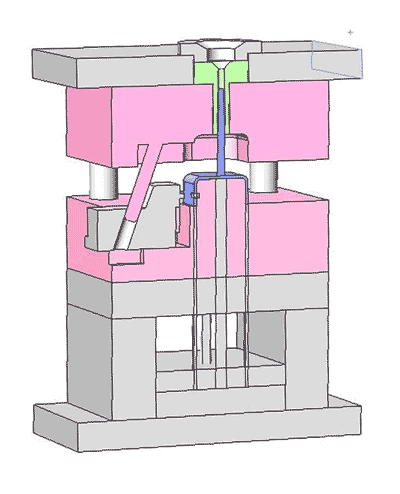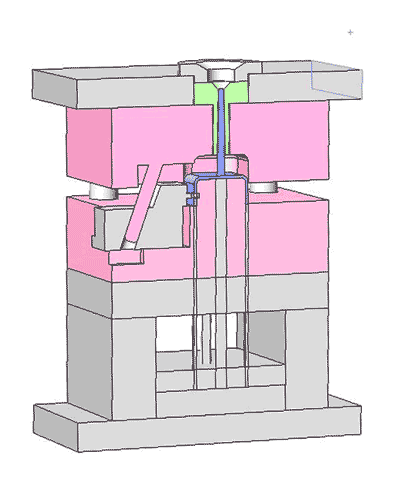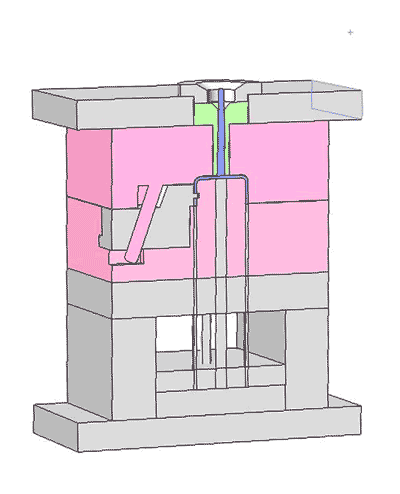
The ejecting mechanism consists of ejector pins and the top and bottom ejector plates, playing a crucial role in seamlessly releasing the formed parts from the mold.
The top ejector plate has many holes for installing and positioning the ejector pins, whereas the bottom ejector plate lacks holes and serves to push the ejector pins.
As the ejector plates move upwards, they drive the ejector pins, which then eject the cooled plastic part from the mold.
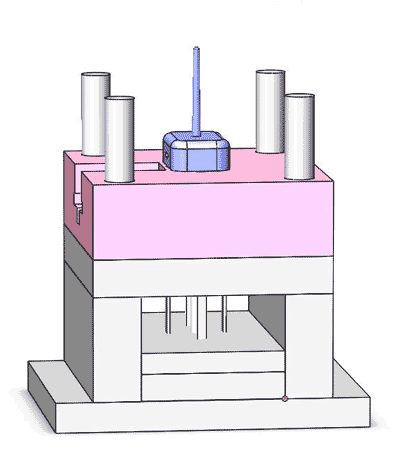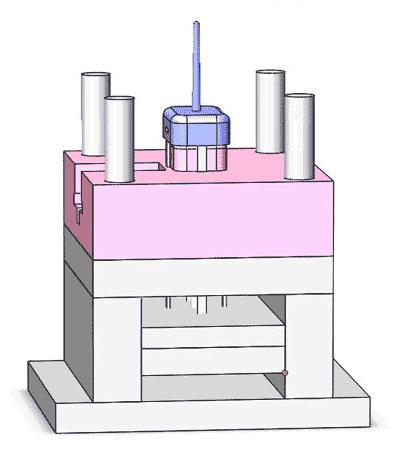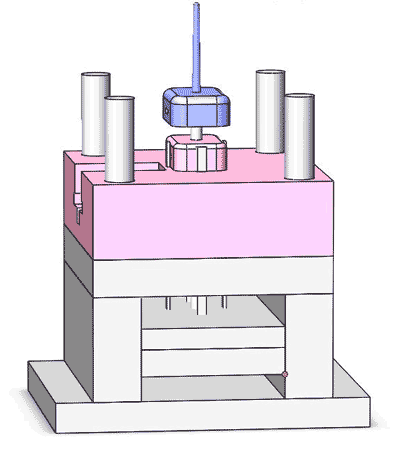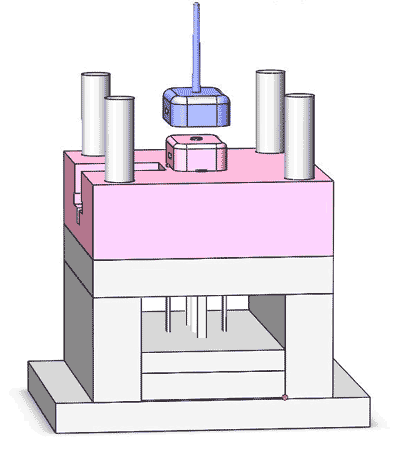
The composition of mold cost
With that being said, we can break down the mold cost like follows:
1. The material cost
The cost calculation of the injection mold starts from the material cost. First, we will calculate the costs of the main steel plates.
The classification of material costs
- The main plates: Core Plate, Cavity plate, slider, clamping plate, spacer blocks, top ejector plate, and bottom ejector plate;
- Slide components: Slider, lifter, cylinders or other sliding mechanisms;
- Accessories: sliding pillars, ejector pins, hot runners (optional), springs, fasteners, etc.
- Auxiliary material: bronze or graphite used as the electrode for EDM.
An example of how to calculate the Cavity Plate
Based on the size of the plastic parts, the number of cavities, and the basic structure (whether there are sliders, cores, two-plate molds or three-plate molds, etc.), we can calculate the size and weight of the steel plates and then get the cost of them.
When the product size is L*W, and there are 2 cavities, then the distance between cavities R, and the distance from cavities to edges T1, T2 can be obtained from empirical formulas, so we can get the length and the width of the cavity plate Lca and Wca,
- Lca=2W+2T1+R
- Wca=L+2T2
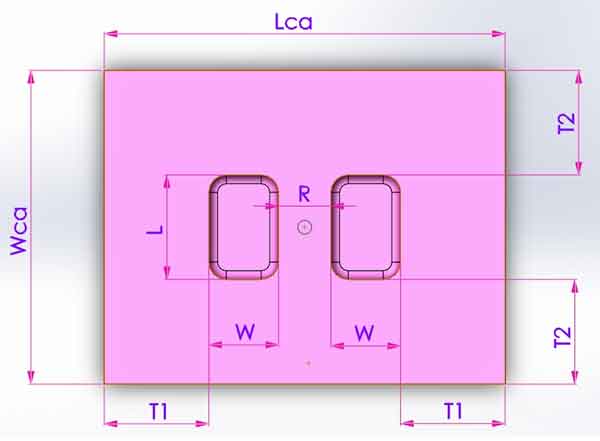
And the height Hca is also calculated by an empirical formula.
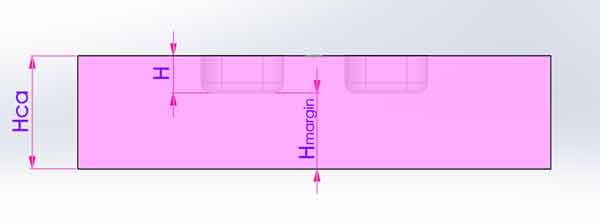
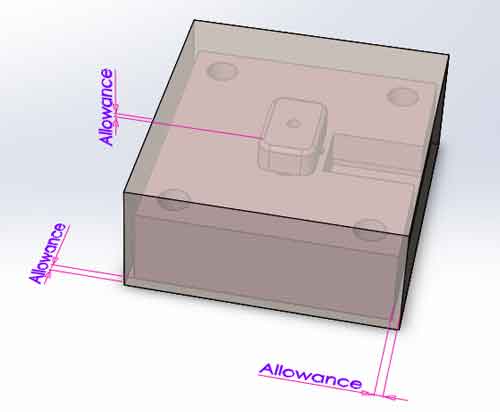
When calculating the raw material dimensions, some allowance needs to be added to the length, width, and height. Then we have the material weight of the Cavity Plate.
Weight of raw material=Length x width x height x 7.85 / 1,000,000 (kg)
(Note: the units are mm, kg in this formula.)
Likewise, we will do the same calculation for the other steel plates and sliding components to get their weight and costs, and add them together.
2. The design fee
A successful plastic molding project starts from a good mold design, which requires a lot of skill and experience and often involves teamwork. Designers, mold makers, and others collaborate and combine their input to find the best option.
Depending on the size and complexity of the mold, the design fee usually ranges from $100 to $300, sometimes could be even higher.
A skillful designer’s hourly rate can be 30 to 40 dollars, this sounds a bit high, but they can finish the design of 8-10 simple injection molds in a day (12 hours), so their charge is reasonable for their output.
3. The machining cost
Machining is the most expensive part of the mold. The cost also depends on the type and grade of the machining equipment. The hourly rate of top brand equipment is 2-3 times higher than that of ordinary equipment.
The formula for calculating machining costs is:
Machining fee = hourly rate X machining time
Since it is hard to estimate the machining time accurately, we can only make an approximation based on the size of the plastic part and the actual processing cost of similar parts in the past.
4. The assembly fee
The mold assembly is time-consuming work. It includes adjusting the dimensions that are not in place during machining, making all the moving parts fit with appropriate tightness, and debugging the issues that were not anticipated in the design stage. The more complex or the more expensive the mold is, the longer it takes to match the mold. For example, a 10,000-dollar worth of mold may take 50-100 hours to match.
However, the time required for mold assembly cannot be precisely estimated either.
5. Tax and profit
Tax and profit: Except for the tax and other overhead fees, a reasonable profit margin should be around 15-30%. Sometimes it may be a little higher for more challenging jobs, the extra profit is for the risk (uncertainty) the mold maker is going to take. Remember the mold manufacturer is responsible for delivering the final result, which is the injection mold that can smoothly produce the plastic parts with good quality, but not merely making a mold that ends up with excessive molding defects.
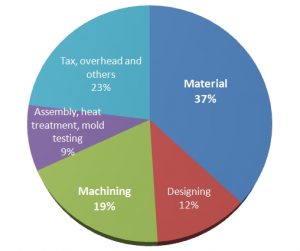
Usual percentage of each costs
It makes sense to know what are the most common percentage of each cost, so you will know if the quotes you receive are calculated properly, and if the prices are competitive:
| Item | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material | 20-35% |
| 2 | Machining | 25-40% |
| 3 | Assembly | 15-20% |
| 4 | Mold design | 5-10% |
| 5 | Tax, profit | 20-30% |
The accuracy of estimation of each cost
Some costs are difficult to be predicted precisely in advance
As mentioned above, some costs, especially machining and assembly fees, cannot be precisely estimated when calculating quotations. Only the fuzzy quotation method can be used. The so-called fuzzy quotation is that it will be the quotation actually slightly upward than the actual cost, but there is also the possibility of downward fluctuation. And the upward and downward fluctuations between different costs may offset each other, to achieve the overall fluctuation is not very large.
| Item | Material | Machining | Design | Assembly, | Tax, Profit |
| Accuracy | (0~+5%) | (-5~+20%) | (-5~+10%) | (-5~+10%) | (0~+5%) |
Ask multiple suppliers to supply the cost break down for cross reference
Before you make the final decision to place the order, it makes sense to ask 2 or 3 suppliers to submit you the cost break down for the mold, so you will know whether the costs have been calculated correctly, and which supplier appears to be more professional in the quote process.
Material cost multiplier quotation method
In the above quotation methods, each cost is estimated separately. But in actual operation, mold factories often use simpler methods, that is to calculate material costs first and multiply by a price factor according to the mold size, complexity of the mold and so forth.
Mold price=Total material cost * price factor
This price factor for a typical injection mold is between 2.5 and 5.
What influences the price factor
The mold size:
As the mold size increases, the Price Factor decreases. Small molds have lower material costs, yet the reduction in other expenses is not as significant. Conversely, with larger molds, the increase in other costs does not scale proportionally with the rise in material costs.
Complexity:
The complexity of the mold directly correlates with its Price Factor; more intricate molds command higher prices.
Simple geometric molds can be efficiently machined using larger milling tools, requiring less time. In contrast, molds with complex shapes necessitate the use of smaller milling tools for detailed work, and some parts may require EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), significantly extending the machining time.
Additionally, more complex molds often feature many sliding mechanisms and require more components for assembly.
Precision:
This is because achieving higher accuracy necessitates the use of more sophisticated and expensive equipment, as well as slowing down the tool’s movement (feeding) to reach the desired level of precision.
Sometimes, adjustments to the mold’s structure are also required to accommodate these precision needs.
Tall ribs and posts
Tall ribs/posts are equivalent to deep grooves/holes within the mold, requiring the application of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). Additionally, this will present challenges during the injection molding process and elevate the manufacturing cost of the components.
Electrodes for EDM:
Certain features require EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) to be completed, utilizing electrodes made from copper or graphite.
Sometimes, electrodes can be made small, but at other times, they must be as large as the entire part. The material costs and machining expenses of these electrodes contribute to an increase in the mold’s cost.
There are many types and grades of hot runners, with prices ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, and they require the use of a temperature control unit. While hot runners offer significant benefits, they also lead to an increase in costs.
The number of cavities:
Molds featuring a higher number of cavities often employ hot runners to ensure even pressure and flow distribution at each gate. Such molds demand greater dimensional uniformity across cavities, posing higher risks for the mold maker. These elements contribute to an increase in pricing.
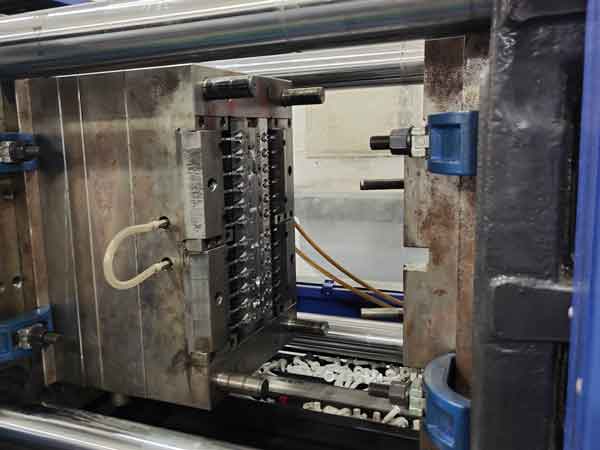
For instance, the type of injection mold depicted in the right-hand image, used for manufacturing dispenser caps, typically costs between $12,000 and $18,000.

The hardness of tool steel:
The hardness of standard mold steel ranges from HRC28 to HRC54. Mold steels with higher hardness require heat treatment followed by precision machining, making the harder molds more expensive due to the longer processing time.
Tip: The hardness of through-hardened molds generally falls between HRC46 – 54. They are used exclusively for high-volume production or with high-temperature plastics such as PPS, PEEK, and PES.
In contrast, the hardness of pre-hardened tools typically ranges from HRC28 – 40. These are made from steel that has undergone a pre-hardening process, eliminating the need for heat treatment and allowing for direct machining to the final dimensions.
An example of a mold cost break down
Now, to help you better understand how the mold cost is calculated, let’s take a look at an example in the table below. Please note that we have given the hourly rate of different processes, so that you can understand how each cost is calculated.
This is a square lid for a plastic box, the basic information is as follows:
♦ Product material: PP
♦ Product dimension: 150*150*15mm
♦ Mold material: 718H
♦ Number of cavities: 1
♦ Ejection method: ejection plate
Our quote for this mold is $1250, the cost breakdown is listed below:
Cost breakdown for an injection mold
(We have hidden the below table for mobile devices. You need to use desktop or tablet devices to view it.)
| Catogory | Item | Description | Unit price | Qty. (unit) | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Mold base (standard) | Material 1045, outer dimension 300*280*260mm, 60 kgs. | $100 | 1 (piece) | $100 |
| Core plate | Material 718H, 280*280*80mm, 50 kgs. | $150 | 1 (piece) | $150 | |
| Cavity plate | Material 718H, 280*280*80mm, 50 kgs. | $150 | 1 (piece) | $150 | |
| EDM electrode (for core) | Copper, 150*150*20mm, 4 kgs | $35 | 1 (piece) | $35 | |
| Accessories | Bolts, hose connectores ,etc. | $50 | 1 (set) | $30 | |
| Designing | Part designing fee | $50 | 1 (piece) | $50 | |
| Mold designing fee | $100 | 1 (piece) | $100 | ||
| Machining | CNC milling | $8/hour | 15 (hours) | $120 | |
| CNC engraving | $4/hour | 10 (hours) | $40 | ||
| Wire EDM | $1.5/hour | 6 (hours) | $9 | ||
| EDM discharging | $3/hour | 10 (hours) | $30 | ||
| Surface polishing | $8/hour | 6 (hours) | $48 | ||
| Assembly, heat treatment, mold testing | Assembly | $8/hour | 10 (hours) | $80 | |
| Heat treatment | $0.5/kg | None | |||
| Mold testing | $20/time | 2 (times) | $40 | ||
| Tax, overhead and others | Tax | $90 | |||
| Administration fee | $95 | ||||
| Profit | $100 | ||||
| Total | $1,267 | ||||
How to use our online mold cost calculator
This online injection mold cost calculator uses the part dimensions, the number of cavities, and the number of slides to calculate the mold dimensions and then estimate the mold price. It is not 100% accurate but can provide a close enough estimation.
Here is the explanation of how to use this mold cost calculator. First, you need to enter the values of the following:
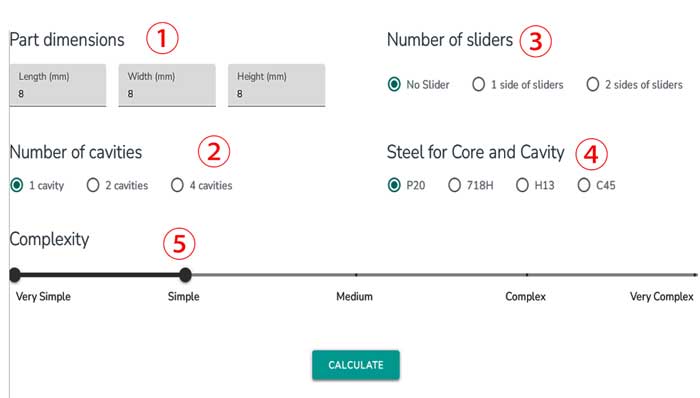
Make sure the length (L) is bigger than the width (W), otherwise, their values will switch automatically.
Note: Maximum value for L, W and H: 600mm
Minimum value for L, W and H: 8mm (please use 8mm if the value is smaller)
There are 3 options: 1 cavity, 2 cavities, and 4 cavities.
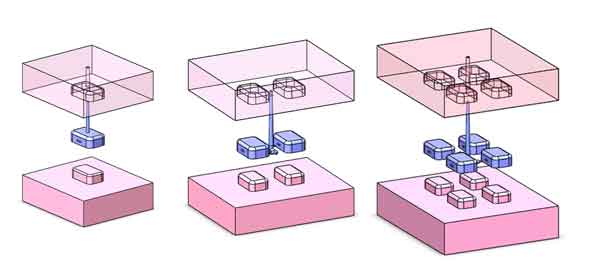
There are 3 options here: no slider, 1 side of sliders and 2 sides of sliders
Note: If there are multiple sliders on the same side, they are considered 1 side of sliders.

For helical gears, please choose 2 sides of sliders because there is a helical ejecting mechanism.
Where P20 – low end; 718H (medium); H13 (high end), these mold steels are the most commonly used.
C45 is also sometimes used in low-end applications.
The complexity levels are divided into five categories: very simple, simple, medium, complex, and very complex. A “simple” classification indicates minimal small details, lower precision requirements, fewer and smaller sliders, and lower ribs. On the other hand, a “complex” classification suggests the presence of more intricate details, higher precision, larger and more sliders, and taller ribs, essentially the reverse of the simple category.
For a comprehensive understanding, please refer to the previously discussed factors that affect the mold’s price factor.
It is advisable to select 2 or 3 levels of complexity to provide a broad price range for a more informative reference.
Here are the outputs of the calculation:
This is the estimation of the mold dimension so you will have a visual conception of how the mold will look like.
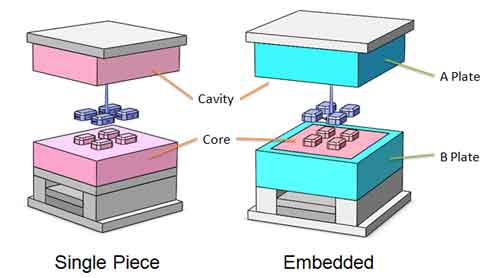
Since the steel for the Core and Cavity are made of more expensive steel, they are often embedded into the A/B plates so they can be made smaller.
The calculator will automatically compare the results of embedded and single-piece designs and choose the better option.
This calculator will give 2-3 prices, each corresponding to a different complexity level, so that you can get a price range that provides a better reference. Each price provides a cost breakdown and their percentage.
These are the results obtained from the simulation calculator. If you would like a more accurate and realistic manual quote, please contact us
Examples for verifying the calculator's accuracy
Here are some examples of mold prices to verify the accuracy of the mold price calculator. It can be seen that for plastic products with general complexity and accuracy, its valuation is still close.

| Part dimensions | Number of cavities | Number of slides | Steel for Core and Cavities | Complexity, |
| 350*135*40 | 1*1 | 1 | H13 | Medium |
| Additional mold information | Calculator Price | Real Price |
| Hot runner, 3 sub-gates | $8450 | $8900 |
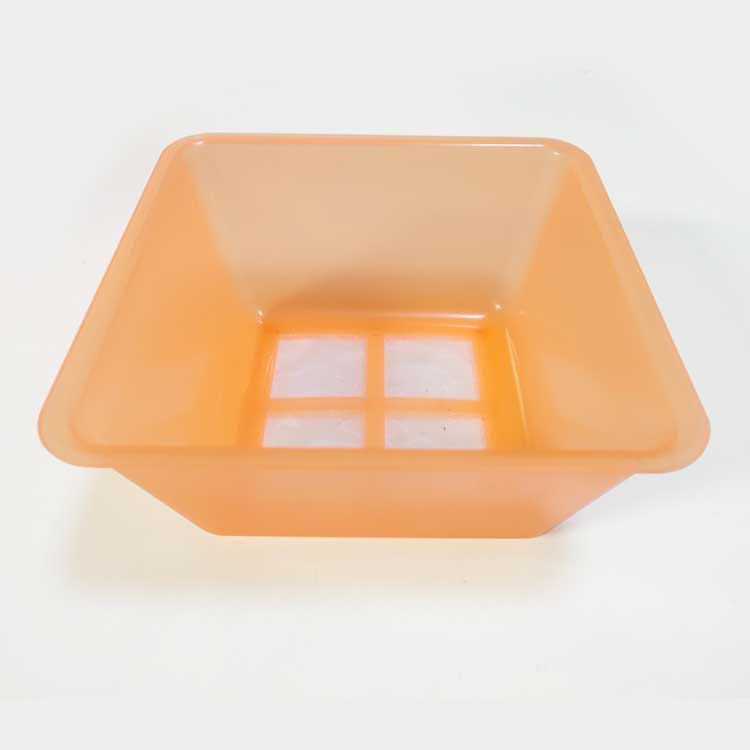

Item name: Storage box with mesh.
Material: PP
| Part dimensions | Number of cavities | Number of slides | Steel for Core and Cavities | Complexity, |
| 150*150*80 | 1*1 | 0 | P20 | Very Simple |
| Additional mold information | Calculator Price | Real Price |
| Cold runner. Ejector plate with air nozzle | $2170 | $2350 |
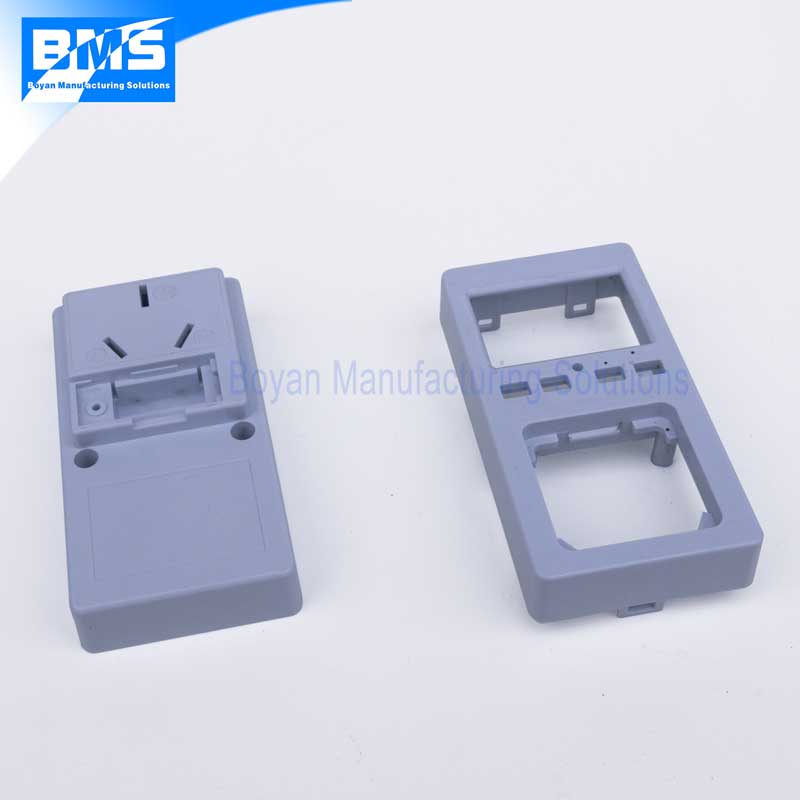

Item name: Plastic case for power socket.
Material: ABS
| Part dimensions | Number of cavities | Number of slides | Steel for Core and Cavities | Complexity, |
| 80*40*40 | 1+1 family | 1 | 718H | Very Simple |
| Additional mold information | Calculator Price | Real Price |
| Cold runner, edge gates | $2290 | $1960 |
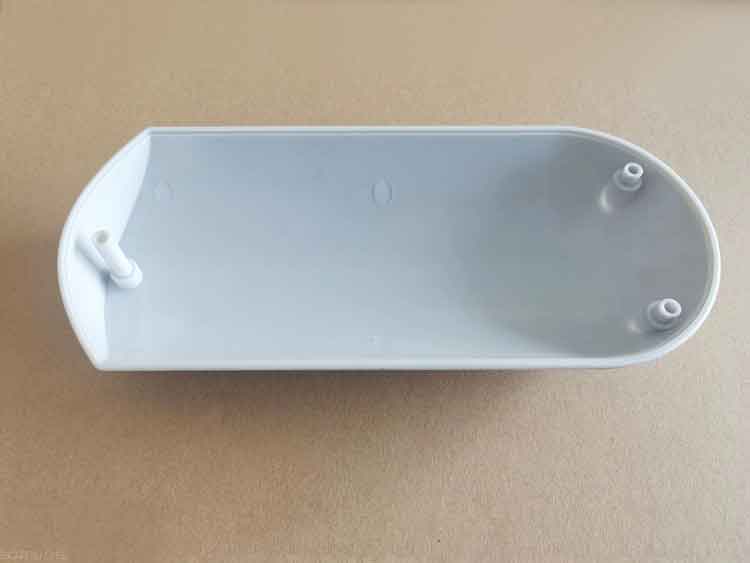

Item name: Plastic enclosure of drive device.
Material: PC
| Part dimensions | Number of cavities | Number of slides | Steel for Core and Cavities | Complexity, |
| 243*105*38 | 2 | 0 | 718H | Simple |
| Additional mold information | Calculator Price | Real Price |
| Cold runner, edge gates | $4965 | $4690 |
However, for some plastic parts with special requirements, the price calculated by this calculator will be low, such as this LED lamp lens, which will give a much lower price than the actual price. This is because the lens has high requirements for the projected light pattern, and its geometric shape accuracy is very high.
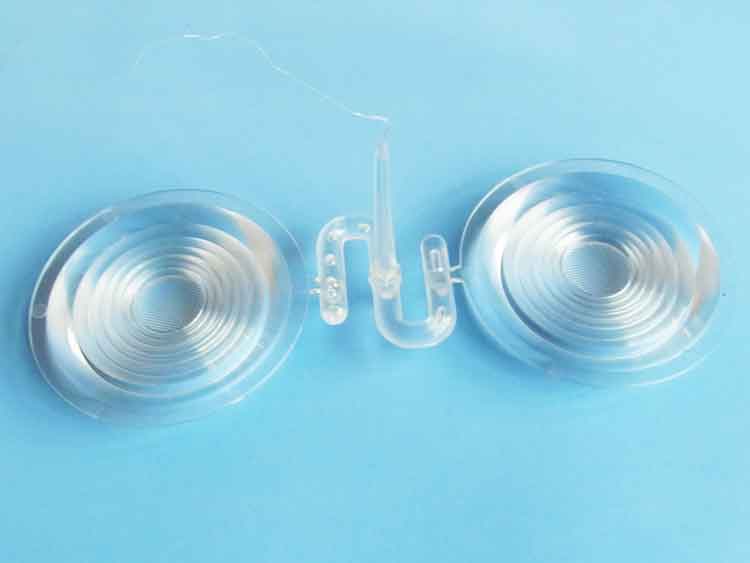

Item name: LED lens.
Material: PC
| Part dimensions | Number of cavities | Number of slides | Steel for Core and Cavities | Complexity, |
| Dia. 50*8 | 1+1 family | 2 | S136 | Very Complex |
| Additional mold information | Calculator Price | Real Price |
| Cold runner, edge gates | $5795 | $11000 |
Frequently Asked Questions
The majority of mold prices fall between $1,000 and $10,000. However, the cost of some large-scale molds, such as those used for automotive parts, can reach several hundred thousand dollars.
Material costs generally constitute 20-35% of the total mold price. However, for some larger and simpler molds, the material costs can represent 60-70% of the total cost, such as the chair shown in the example below.

If a small mold manufacturer quotes a base price, a medium-sized manufacturer may quote 1.5 to 2 times that amount, while a large manufacturer might quote 2 to 2.5 times the base price. This variation is due to differences in overhead costs and profit expectations among the manufacturers.
Not necessarily.
Small mold manufacturers may devote more attention to each project, but their capabilities vary widely. Some may lack the necessary skills to achieve quality results, so discernment is crucial.
Medium-sized manufacturers might offer less focus on your project and cannot guarantee their technical proficiency, similar to smaller factories.
Large mold manufacturers possess strong technical capabilities, yet they may not prioritize your project as highly. Although the risk is lowest with large manufacturers, collaboration with them might lack flexibility and adaptability.
Therefore, the answer to this question is not absolute and requires thorough due diligence.
To quickly assess mold quality, consider the following aspects:
The rationality of the design, such as the design of the gate and the arrangement of cooling channels; the precision of the machining, with minimal marks from later refinements; and a manual test of pushing the ejector plate, which should move smoothly, indicating overall machining accuracy.
Several approaches can help lower mold costs, including:
- Intelligent product design, such as reducing undercuts and lowering rib heights, which can simplify the mold design.
- Utilizing family molds, which can decrease the total number of molds needed.
- Choosing appropriate mold steel materials. For some molds, a lower grade material can be used for the core since the cavity is more prone to wear and tear, leading to burrs.
- Lastly, partnering with the right mold manufacturing facility is crucial.
The cost of molds based on weight typically ranges from $8 to $50 per kilogram. This variation is influenced by the type of steel used for the mold, as well as the mold’s complexity and size.
Although the price of mold steel, which ranges from $2 to $20 per kilogram, might suggest that mold costs are relatively high, this isn’t necessarily the case. Material costs alone can make up 20% to 35% of the total mold price, and can even surpass 50%.
This is due to the fact that pricing is based on the mold’s net weight, yet the actual material used often exceeds this amount. Furthermore, the pricing doesn’t account for mold accessories, which are sold as complete products not priced by weight, nor does it include the materials for electrical discharge machining (EDM), such as copper or graphite electrodes. These factors add complexity to the mold’s pricing structure.