Table of Contents
ToggleWelcome to Boyan's Painting Services for Injection Molded Parts!
At Boyan, we take pride in offering a comprehensive range of painting services tailored to various types of plastic materials and surface finishes.
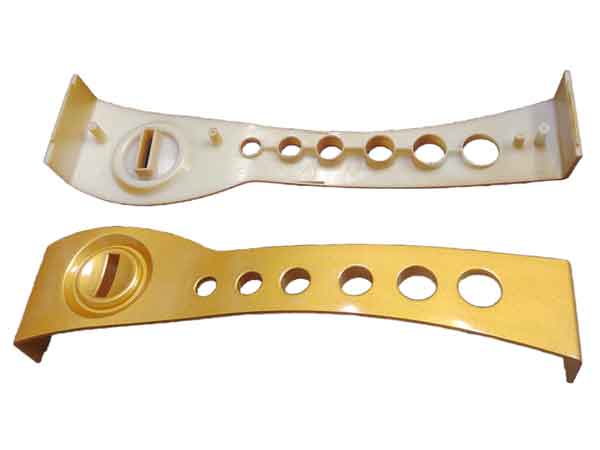
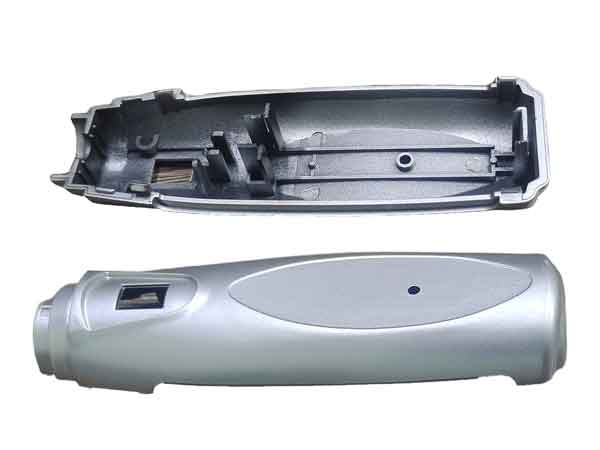
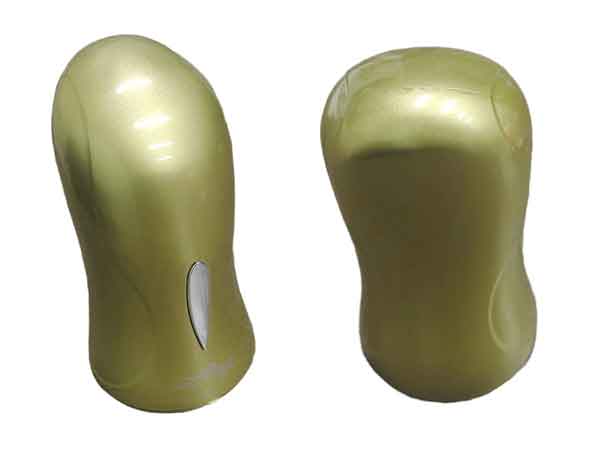






In this post, we will give you a thorough introduction to our painting services for plastic parts. Whether you’re in the automotive industry, home appliances, daily goods, or furniture and so forth, our painting solutions are designed to enhance your products in numerous ways.
First, let’s understand the pros and cons of plastic parts painting:
Advantages of Painting Plastic Parts
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Painting can provide colors and glossiness beyond the natural capabilities of plastic materials, significantly boosting the visual appeal of products.
- Increased Hardness and Scratch Resistance: Many types of paint offer a hardness surpassing that of the underlying plastic, making surfaces less prone to scratching.
- Soft Touch and Feel: Some paints add a degree of softness, offering a unique tactile experience.
- UV and Chemical Resistance: A coat of paint acts like armor against UV rays and chemical corrosion, prolonging the lifespan of the product.
- Concealing Injection Molding Flaws: Paint can hide certain imperfections from the injection molding process, such as weld lines, gate blush, and discoloration, resulting in a more uniform surface appearance. However, it’s worth noting that paint cannot conceal surface irregularities like sink marks, floating fibers, or severe weld lines.
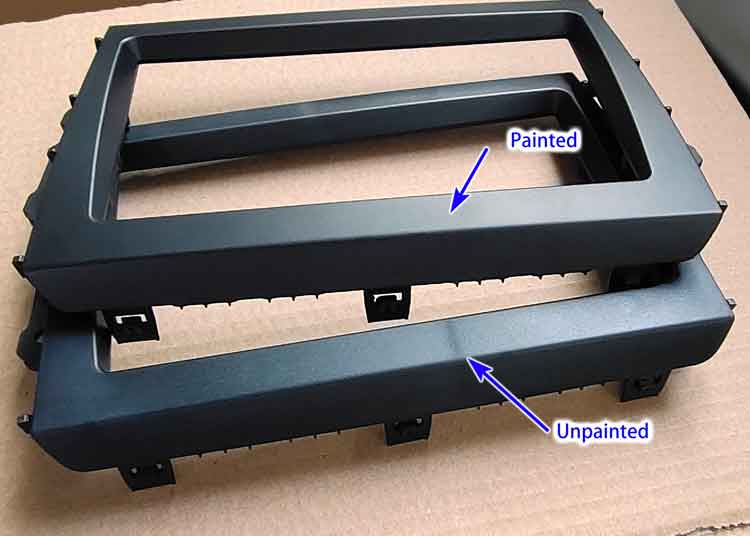
Considerations and Challenges
Despite its benefits, painting plastic parts comes with its own set of challenges that need careful consideration.
- Additional Costs: The painting process involves multiple manual steps including product retrieval, pre-inspection, painting, quality inspection, and packaging. Compared to the high automation level of injection molding, painting inevitably leads to higher production costs.
- Recycling Concerns: While untreated injection molded products can be ground up and recycled, painted plastic products face recyclability issues. Once painted, these products cannot be recycled in the same way, especially after their lifecycle ends.
- Risk of Higher Scrap Rates: Painted plastic products are subject to additional quality requirements, such as appearance, adhesion, and hardness. Failure to meet these criteria can lead to a significant increase in scrap rates, underscoring the importance of preliminary sample or small batch testing.
Quality Inspection Standards for Painted Plastic Products
When it comes to painted plastic products, while appearance is undoubtedly crucial, there are several other key tests designed to ensure the paint layer meets high standards of quality and durability. Here’s a breakdown of some common inspection items and testing methods:
Adhesion Test: Cross-Cut (Grid) Test
One fundamental test is the adhesion or cross-cut test. It involves scoring the paint surface with a grid pattern using a utility knife (though a specialized cross-cut knife is often used) and then applying and rapidly removing adhesive tape over the grid. The extent to which the paint is peeled off by the tape gives a measure of the paint’s adhesion strength. The specifics of this test and its grading criteria can be found in the ASTM D3359 standard.
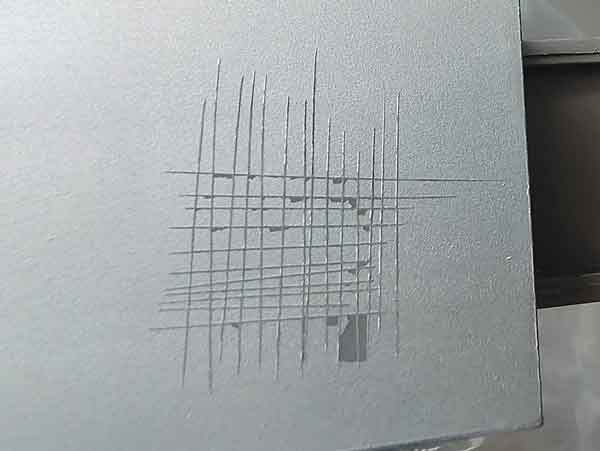

(The cross-cut test isn’t a one-time procedure; it needs to be conducted regularly, at least once for every production batch. For instance, adjustments in the material of a product might result in the test failing. Additionally, parts of the surface may have poor adhesion, indicating that issues can be localized.)
Paint Hardness: Pencil Scratch Test
The pencil scratch test assesses the hardness of the paint layer. Different grades of pencils, such as H, 2H, or 3H, are used to determine the hardest pencil that does not leave a scratch on the painted surface. This test helps ensure the painted surface can resist scratches to a certain degree.
Wear Resistance: RCA Tape Test
To evaluate the paint’s resistance to wear, the RCA tape wear test is used. The painted item is placed under an RCA paper tape wear testing machine set to a specific number of cycles. After the test, the item is examined for any damage to the paint layer, providing insight into its durability against wear.

Solvent Stability: Alcohol Rub Test
The alcohol rub test involves using a cloth soaked in alcohol to rub the painted surface for 1-2 minutes. After rubbing, the surface is checked for damage, color changes, softening, or peeling. This test assesses how well the paint layer can withstand exposure to solvents.
Additional Testing
For products that require further assurance of their paint layer’s quality, additional tests like the salt spray (fog) test for corrosion resistance and UV aging tests for UV stability can be performed. These tests help in understanding how the paint layer reacts to harsh environmental conditions, ensuring the product remains durable and maintains its appearance over time.
In summary, ensuring the quality of painted plastic products involves a series of standard tests, each designed to evaluate different aspects of the paint layer’s performance. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can deliver products that not only look good but also stand up to the demands of everyday use.
Guide to Choosing Paint and Painting Methods for Different Plastics
Plastics and paints interact in diverse ways, largely due to the varying chemical compositions of the plastics themselves. Let’s break down how to select the right paint and approach for different types of plastic materials.
Easy-to-Paint Plastics:ABS and PS
- Characteristics: These plastics have higher surface tension and polarity, which makes them more receptive to paint.
- Painting Method: They can be directly painted without needing a primer, ensuring good adhesion and durability of the paint.
Challenging-to-Paint Plastics:PP and Nylon
- Characteristics: These materials have lower polarity and surface tension, making paint adhesion more difficult.
- Painting Method: A specialized primer or adhesion promoter is necessary before applying the topcoat to ensure the paint adheres well.
Common Types of Paint for Plastics
- Polyurethane Paint: Known for its durability and resistance to chemicals and abrasion.
- Acrylic Paint: Offers a glossy finish and fast drying times.
- Fluorocarbon Paint: Excelling in weather resistance, ideal for outdoor applications.
- PP Paint: Specially formulated for painting polypropylene materials.
- UV Paint: Cures under UV light, offering a durable and high-gloss finish.
Paint Formulations
- Single-component Paint: Easy to use, requiring no mixing, but may not be as durable as two-component systems.
- Two-component Paint: Consists of a base and a hardener, providing superior durability and resistance.
Special Considerations
For some plastics, specific paints are designed to meet their unique needs. It’s important to choose the right type of paint to ensure not only aesthetic appeal but also long-term performance and adherence.
How to Choose the Right Paint Shop in China
Finding a suitable paint shop in China can be quite challenging given the diverse range of sizes and management levels among the factories. Here’s a guide on navigating through the options to find the right match for your painting needs.
Understand the Craftsmanship
Many painters in the industry started as apprentices, relying more on experience than formal training. This means while they may be skilled, they might lack theoretical knowledge about painting. To bridge this gap, it’s wise to consult with paint suppliers who can provide professional insights and recommendations.
Evaluate the Size and Equipment
Paint shops vary significantly in size and the types of equipment they possess, which can affect the quality and speed of the painting process.
Types of Painting Equipment
- Manual Spray Painting: Good for custom or small-batch jobs but can be inconsistent.
- Robotic Spray Painting: Offers precision and consistency, ideal for high-volume production.
- Automated Multi-station Spray Systems: These systems provide high efficiency and uniformity for larger operations.
Curing and Drying Equipment
- Conveyor Ovens: For efficient, continuous production.
- Batch Ovens: Suitable for smaller quantities or larger items.
- UV Curing Systems: For quick curing of UV-sensitive paints.
Workshop Environment
- Dust-Free Workshops: Essential for high-quality finishes, free from impurities.
- Standard Workshops: Might be more prone to dust and debris, affecting the paint quality.
It’s important to note that the paint used for plastics is a type of low-temperature paint, which dries quickly on the surface. Therefore, it’s less sensitive to dust and debris, and generally, operations do not require a dust-free workshop environment.
Comprehensive Consideration
When selecting a paint shop, consider their equipment, workshop conditions, and the expertise of their staff. Don’t hesitate to visit the facilities in person, if possible, to assess their capabilities and discuss your specific needs to ensure they can meet your quality standards and deadlines.
Quality control in Plastic Painting Processes
Working with plastic painting factories presents unique challenges, especially considering the high volume of products processed daily. Since painted plastic items cannot be recycled, every step must be approached with care to avoid or minimize quality risks. Here are some strategies to help ensure the success of your plastic painting projects.
Preparing Products for Painting
- Quality Assurance Before Painting: Before the painting process begins, it’s crucial to prepare the plastic items properly. This involves trimming gates, sanding any defects, and conducting a thorough visual inspection. While paint shops also perform their inspections, these are most effective when the defect rate is already low to not disrupt the painting schedule.
- Strategic Gate Placement: Ideally, gates should be placed in areas that are not visible to avoid aesthetic issues. If design constraints necessitate gates in exposed areas, manual trimming is necessary to ensure a clean finish.
- Surface Cleanliness: The products to be painted must be free from mold release agents and greasy residues, as these can significantly affect paint adhesion. Handling the products with gloves is recommended to maintain surface readiness for painting.
- Increased Visibility of Defects: It’s important to remember that painting will enhance the product’s appearance, making even minor imperfections more noticeable. Thus, a meticulous pre-painting inspection is crucial to identify and rectify any flaws.
Ensuring Quality Control During Painting
- On-Site Supervision: Many painting factories may lack a robust quality control system or the personnel needed for thorough inspections. Having a member of your team present on-site, especially at the start of the painting process, is advisable. Follow-up checks should be conducted randomly to ensure ongoing adherence to quality standards.
By implementing these practices, you can effectively manage the inherent challenges of plastic painting and ensure that your products meet the highest quality standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carrying out plastic parts painting requires a high degree of carefulness and concentration., from preparation to the final inspection. By understanding the challenges and adopting best practices for quality control, businesses can enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of their products. Success in plastic parts painting hinges on meticulous preparation, strategic planning, and ongoing supervision, ensuring each piece meets the highest standards of quality and finish

