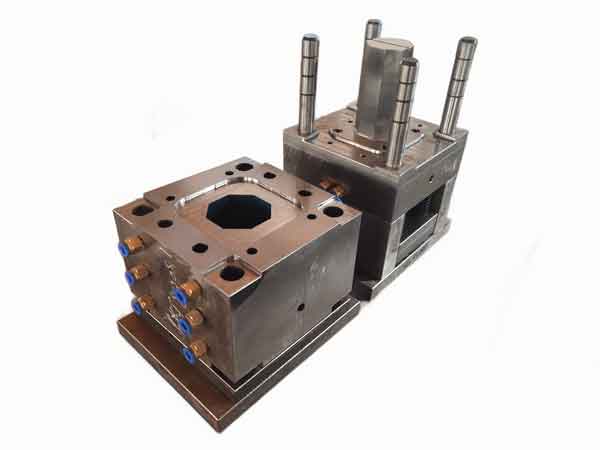
When you source molds from China, you’re often faced with a pivotal decision: Do you intend to keep the mold in China for production, or do you plan to transport it to your country for manufacturing? This decision arises from the fact that there are distinct differences in the manufacturing standards and requirements for these two scenarios.
For the sake of clarity in our discussion, let’s refer to molds shipped to international clients as “Export Molds” or “Export-Grade Injection Molds,” while those retained in China for production are termed “Domestic-Use Molds.” In the following sections, we will delve into the specific distinctions between these two types of molds
Export Molds vs. Domestic-Use Molds: Key Differences
The main distinction between export molds and domestic-use molds lies in the stricter requirements for export molds due to their use in other countries.
- Firstly, export molds demand higher reliability. This is crucial because if issues arise, repairs can be more challenging and expensive for international clients.
- Secondly, these molds adhere to higher standards in the universality and interchangeability of parts, facilitating easy replacement of damaged components when necessary.
This implies that export molds are crafted with greater precision in design and manufacturing, often utilizing superior materials and processes to ensure long-term stability and durability.
On the other hand, domestic-use molds emphasize ease of maintenance. As these molds operate within China, any malfunctions can be quickly addressed and rectified. Consequently, these molds might prioritize cost efficiency and flexibility in their production, allowing the use of more economical materials and simpler designs.
While this does not imply a compromise in quality, the focus for domestic-use molds may lean more towards cost control and adaptability in their design and production processes.
Detailed Contrast Between the Export Molds to Domestic-Use Molds:
Let’s explore in more detail the differences between these two categories of molds:
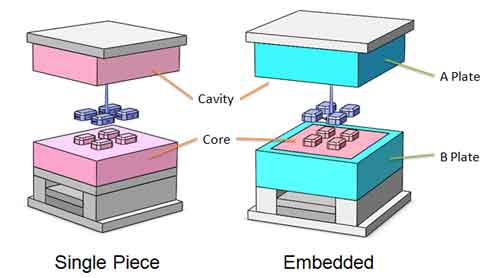
Mold Structure
Domestic-Use Molds: When producing products that are smaller in size and limited in quantity, domestic-use molds opt for a single-piece core structure. This single-piece core structure means that there is no embedded frame around the core and cavity, making the design straightforward and practical. It’s well-suited for small-batch production and is also more cost-effective to manufacture and maintain.
Export Molds: In contrast, export molds typically employ an embedded core structure. This means that the core part of the mold is set within A/B plates, which are usually part of the mold’s framework. The embedded structure is advantageous because it is more appropriate for mass production and conforms to mold design standards, thereby enhancing the mold’s durability.
Common Mold Components
When it comes to mold components, the parts we primarily consider include Ejector Pins, Guide Pins and Bushings, Cooling System Components, Limit Switches, Hot Runner Systems, Lubrication Systems, and more.
The choice of these components differs between domestic-use molds and export molds:
Domestic-Use Molds: These molds typically select components that conform to Chinese standards. With cost, availability, and local market needs in mind, molds intended for domestic use tend to utilize standard parts supplied by local vendors.
Export Molds: The design and manufacture of export molds require confirmation with the client regarding which standard of components to use. This often depends on the target export market.
For instance, molds exported to Europe usually adopt components that meet HASCO standards, while those sent to the USA are more likely to choose parts that comply with DME standards. Such choices are made to ensure that the molds meet the specific requirements and standards of the target market, which also helps to enhance the mold’s international universality and compatibility.

Optional Mold Components
Domestic-Use Molds: In the design of these molds, the decision to use components such as balance blocks, wear plates, and parting locks primarily depends on the quantity of production.
For projects with small production volumes, it might not be necessary to incorporate all these components, which can reduce costs and simplify the design.
However, for larger production runs or as dictated by product design requirements, these components may be included in the mold design.
Export Molds: Export mold designs typically consider the use of balance blocks to ensure the even and stable operation of the mold. The use of wear plates is determined based on the specific situation and needs of the mold.
Additionally, during the design process of export molds, it is common to confirm with clients whether components like cycle counter, parting locks, thermal insulation plates and even internal temperature sensors are needed.
This is because export molds are aimed at the international market, and their design needs to be more meticulous and comprehensive to meet higher quality standards and the specific demands of clients.
Mold Trial Runs
The trial run process for domestic-use molds and export molds differs in the number of trials and specific procedures:
Domestic-Use Molds: For those intended for domestic use, typically only standard trial runs are needed. These usually include basic injection molding process tests to ensure that the mold can produce products as per the design requirements. Such trials are generally focused on verifying the mold’s fundamental functionality and production efficiency.
Export Molds: In comparison, the trial process for export molds often requires 1 to 2 additional runs beyond the standard trials.
Particularly in the final trial, the mold should be run for about 4 hours to ensure that there are no issues during prolonged operation, affirming the mold’s stability and durability.
Additionally, a manual test to push the ejector plate is conducted to guarantee that it moves smoothly without any obstruction. While domestic-use molds may also undergo this requirement, the testing for export molds is usually more rigorous and detailed, meeting the high standards of mold quality and reliability expected in the international market.
Packaging
There are distinct differences in the packaging methods for domestic-use molds compared to export molds:
Domestic-Use Molds: For molds used domestically, packaging is typically not required. For long-term storage, the main precaution is to spray the core/cavity surfaces with anti-rust oil to prevent corrosion. The exterior may be painted to add a protective layer and shield the mold from environmental damage.
Export Molds: The packaging process for export molds is more complex. Similar to domestic molds, the core surfaces are sprayed with anti-rust oil before shipping to prevent corrosion during transit. Whether external painting is required depends on the specific requirements of the client.
Additionally, export molds are generally wrapped in stretch film for preliminary packaging and then encased in wooden crates for secondary packaging, providing extra protection to ensure the mold’s safety and integrity during long-distance transportation.
Overview in a Table
Below is a concise comparison table summarizing the key points we’ve covered:
| Feature | Domestic-Use Molds | Export Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Structure | Sometimes Single-piece core structure, economical for small batches | Embedded core structure, durable for large-scale production |
| Mold Components | Standard parts conforming to Chinese standards, local suppliers | International standards like HASCO or DME, depending on export market |
| Optional Components | Balance blocks, wear plates, etc., used based on production quantity | Commonly includes balance blocks, cycle counter, wear plates, and confirms need for other parts with clients |
| Trial Runs | Standard trial runs focused on basic functionality and efficiency | Additional trial runs for ensuring stability and durability, detailed ejector plate movement tests |
| Packaging | Anti-rust oil spray for storage, optional painting for extra protection | Anti-rust oil, initial wrap in stretch film, secondary wooden crate packaging for transit protection |
Special Requirements for High-End Molds
In industries like automotive and electronics, the quality standards for molds are exceptionally stringent. These specific requirements include:
High-Speed Milling: All parts must be completed through high-speed milling without any grinding marks, and precision must be kept within the range of 0.005 to 0.01. Unlike standard molds, these high-precision molds don’t require manual dimension adjustments post-processing; they are ready for assembly immediately, which consequently incurs higher production costs.
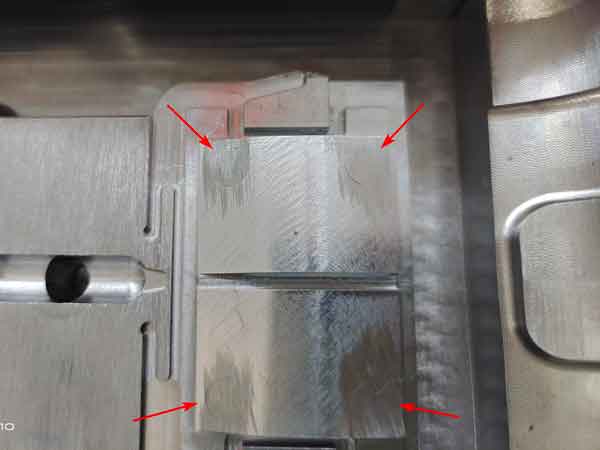

Conformal Cooling Channels: Traditional molds often feature cooling channels made by straight drilling, which can lead to uneven cooling due to hard-to-reach areas. With the advent of 3D printing technology, cooling channels of any shape can be created internally, effectively remedying this issue.
Material Selection for Molds: High-specification molds typically utilize P20 steel for the mold base as opposed to the more common 45# steel used in standard molds. Moreover, materials with higher hardness and more stringent heat treatment requirements, such as those with a hardness level of HRC48-50, are selected.
Mold Components: High-specification molds tend to use components from top-tier brands and are equipped with a richer configuration. When balancing quality against cost, these molds tend to favor the former.
In summary, high-end injection molds demand high technical and quality standards and can justify the increased costs associated with them. This is because in these sectors, any minor quality issues cannot be risked, as the industries cannot afford the losses associated with production downtime.
Boyan's Checklist for Export Molds
Boyan has extensive experience in producing export molds, adept at achieving the optimal balance between cost and quality while ensuring the performance of the molds.
If you have procurement needs for export molds, we recommend referring to the following checklist to ensure you select high-quality molds that meet your requirements:
| Item | Detail |
|---|---|
| Common Mold Accessories | Decide whether to choose accessories that meet HASCO or DME standards, including specified brands and specifications. |
| Optional Mold Components | Choose whether the following mold components are needed: Parting Locks, Thermal Insulation Plates, or other components. |
| Mold Manufacturing Technical Requirements | Determine whether it is necessary to meet HASCO or DME standards, including mold materials, heat treatment, dimensions, and geometric tolerances, etc. |
| Trial Run Requirements | Decide whether to provide detailed trial mold reports and videos, including injection molding parameters, specific material brands used, and the mold’s usage and maintenance manual. |
Boyan is committed to providing you with high-quality, high-performance, and cost-effective export mold solutions. We look forward to collaborating with you to achieve your project goals.


